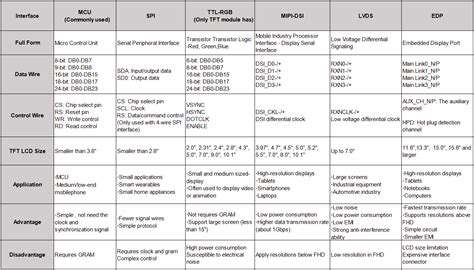
Data Minimization: Collecting Only Necessary Information
Data minimization is a fundamental aspect of data privacy, focusing on gathering and processing only the data essential for a specific, legitimate purpose. This approach minimizes the potential for misuse or unintended consequences of personal data. It involves carefully assessing the data needed for a particular function and avoiding the collection of unnecessary details. By limiting the scope of data collection, organizations can significantly reduce the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access.
A practical example of data minimization involves thoroughly evaluating each data point. Instead of collecting a broad range of information, businesses should focus on gathering only what is directly relevant to their objectives. For instance, if a company aims to track customer preferences for marketing purposes, it should collect only the data necessary to identify those preferences, avoiding irrelevant details like age or income if they are not directly related to the campaign.
Purpose Limitation: Defining Clear and Specific Purposes
Purpose limitation is closely tied to data minimization. It requires clearly defining the specific and legitimate reasons for collecting and processing data. This principle demands a precise understanding of how the data will be used and the potential outcomes. By explicitly stating the intended use of the data, organizations demonstrate accountability and transparency. This fosters trust among data subjects and helps prevent the data from being used for unauthorized purposes.
Additionally, defining clear purposes prevents data from being repurposed or combined with other datasets in unexpected ways. This is a critical aspect of data security and privacy. Organizations must document the purposes for which data is collected, ensuring any future use aligns with these predefined purposes. This meticulous approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
The Interplay Between Minimization and Limitation
Data minimization and purpose limitation are interconnected and reinforce each other. Data minimization ensures only necessary data is collected, reducing the volume of data at risk of misuse. Purpose limitation defines the specific contexts in which the data can be used, preventing unauthorized applications. Together, these principles create a strong framework for managing personal data, promoting accountability, and protecting privacy rights.
Implementing these principles requires a proactive approach to data handling. Organizations must evaluate each data collection practice to ensure it aligns with both minimization and limitation. This includes establishing robust data governance policies, conducting regular reviews of data processing activities, and engaging with data subjects to maintain transparency and compliance.
By understanding the relationship between these principles, organizations can build a more secure and compliant data management system. This fosters trust between organizations and individuals, safeguarding privacy and promoting ethical data practices.
Failure to adhere to these principles can result in significant legal and reputational risks. Organizations must be diligent in their data handling, ensuring every step aligns with data minimization and purpose limitation to uphold privacy and build trust.
Robust Security Measures: Protecting Data from Unauthorized Access
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing sensitive data. This significantly lowers the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. Implementing MFA across all systems, from email to cloud storage, is essential for strengthening data protection and ensuring only authorized individuals can gain access. This proactive measure is a cornerstone of effective security practices.
Employing Strong Encryption Techniques
Data encryption is a fundamental security practice that makes sensitive information unreadable to unauthorized parties. By converting data into an encoded format, encryption ensures hackers cannot decipher it, even if they access the storage location. Using strong encryption algorithms and regularly updating protocols is critical for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity.
Robust encryption protocols, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), ensure data remains protected throughout its lifecycle, from transmission to storage.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in security systems. These evaluations help detect vulnerabilities that unauthorized actors might exploit and provide a plan for implementing countermeasures. Proactively identifying security gaps is crucial for maintaining data integrity and protecting sensitive information. The insights from these audits help organizations prioritize security investments and allocate resources effectively.
Establishing Clear Data Access Policies
Creating clear and comprehensive data access policies defines who can access specific data and under what conditions. These policies should be well-documented, communicated to all relevant personnel, and regularly updated to reflect evolving security needs. This approach ensures data access is restricted to authorized individuals, reducing the risk of breaches and unauthorized disclosures. By implementing granular access controls, organizations can mitigate risks associated with insider threats and accidental data leaks.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee training and awareness programs are vital for fostering a security-conscious culture within an organization. These programs should educate employees about security threats, best practices for data protection, and the importance of adhering to security policies. Regular training sessions help employees recognize and report suspicious activities, preventing phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. This proactive approach to security encourages vigilance, making employees active participants in maintaining data integrity.