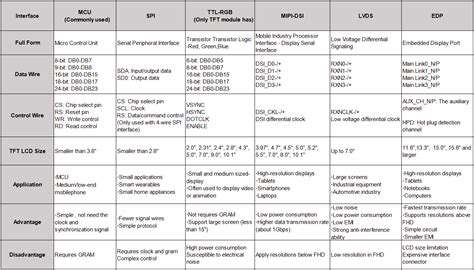
Importance of Standardized Safety Protocols
Safety standards evolve alongside technology, requiring continuous refinement. Current protocols for autonomous vehicles often borrow from aviation and rail industries, but unique challenges demand specialized approaches. Extreme weather testing, for instance, has emerged as a critical evaluation area.
Regulators increasingly emphasize scenario-based testing over simple mileage metrics. This shift better assesses how systems handle complex, real-world situations beyond controlled environments.
Testing Methodologies and Their Significance
Advanced simulation platforms now complement physical testing, allowing evaluation of millions of virtual miles. This dual approach identifies rare but critical edge cases that might take years to encounter in real operation. However, validation of simulation accuracy remains an active research area.
Some jurisdictions now require shadow mode testing, where autonomous systems operate passively alongside human drivers to compare performance before receiving full authorization.
Compliance with Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory landscape varies significantly by region, creating compliance challenges for manufacturers. Some companies adopt the strictest standards globally to simplify certification across markets. This approach, while costly, prevents last-minute adjustments for different jurisdictions.
Third-party certification is gaining traction as a way to ensure impartial evaluation of safety claims. Independent auditors verify testing procedures and results before regulatory submission.
International Harmonization of Safety Standards
Divergent national standards create market fragmentation and slow technology adoption. The UN's World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations has made progress, but key differences remain. Regional blocs like the EU have achieved greater consistency internally.
Standardizing terminology proves surprisingly challenging. Different countries define autonomous capability differently, complicating cross-border comparisons.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Safety protocols must evolve as real-world experience accumulates. Many systems now incorporate over-the-air updates to address newly identified risks without physical recalls. This requires careful version control and change management procedures.
Some regulators have implemented learn and confirm frameworks where initial approvals are granted with requirements for ongoing performance reporting and system updates.

Data Privacy and Security: Protecting Passenger Information
Data Minimization: Collecting Only Necessary Information
Modern privacy frameworks increasingly mandate purpose limitation - collecting only data essential for specific functions. Transit systems face particular challenges as location data alone can reveal sensitive personal patterns. Some agencies now implement automatic data expiration after short retention periods.
Robust Access Controls: Limiting Data Visibility
Role-based access systems have become more sophisticated, with dynamic permissions adjusting based on context. Some systems now incorporate behavioral biometrics to detect and prevent credential misuse by authorized personnel.
Encryption: Protecting Data in Transit and at Rest
Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms are being tested for future implementation. Current best practices mandate encryption even for internal communications between vehicle components. Hardware security modules provide added protection for cryptographic keys.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Continuous monitoring has replaced periodic audits in many systems. Automated tools now detect anomalies in real-time, allowing preemptive response to potential breaches. Bug bounty programs complement internal testing by engaging external security researchers.
Incident Response Plans: Preparing for Data Breaches
Modern response plans incorporate forensic preservation requirements and detailed communication protocols. Many jurisdictions now mandate breach notification within strict timelines, with escalating penalties for delays. Tabletop exercises help teams prepare for various scenarios.
Employee Training and Awareness: Educating Your Workforce
Training now emphasizes practical simulations over theoretical instruction. Phishing tests with realistic scenarios have proven particularly effective at changing behavior. Some organizations tie security compliance to performance metrics.
Data Retention Policies: Managing and Deleting Data
Automated data lifecycle management tools enforce retention policies consistently. Secure deletion methods now include multiple overwrite passes and physical destruction verification for sensitive media. Audit trails track all data disposition actions.
Infrastructure Considerations and Public Acceptance: Paving the Road for Autonomous Transit

Network Infrastructure
5G deployment is enabling vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication at scale. Dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) networks provide fallback options where cellular coverage is unreliable. Edge computing reduces latency for safety-critical decisions.
Server Infrastructure
Distributed computing architectures improve resilience by avoiding single points of failure. Some operators now deploy mobile data centers in transit hubs to reduce backbone network dependencies. Containerization allows efficient resource utilization across applications.
Data Storage Infrastructure
Hierarchical storage management automatically moves less frequently accessed data to cheaper media. Immutable storage options prevent tampering with critical operational logs. Geographic distribution protects against regional outages.
Security Measures
Zero-trust architectures verify every access request regardless of origin. Hardware-based root of trust provides tamper-proof device identity verification. Continuous authentication monitors sessions for suspicious activity.
Power and Cooling Infrastructure
Renewable microgrids increase resilience while reducing environmental impact. Liquid cooling solutions enable higher density deployments in space-constrained transit depots. Predictive maintenance prevents unexpected failures.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Automated failover systems minimize service interruption during outages. Some operators maintain pre-configured mobile units that can rapidly deploy to replace damaged infrastructure. Regular drills ensure staff familiarity with emergency procedures.