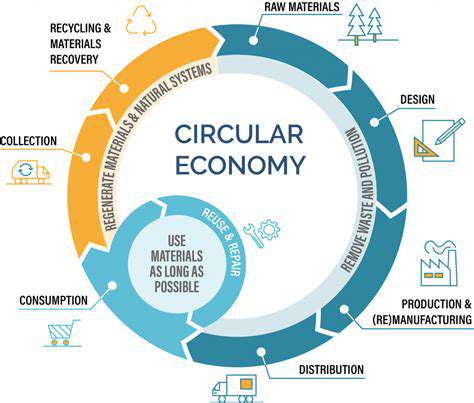
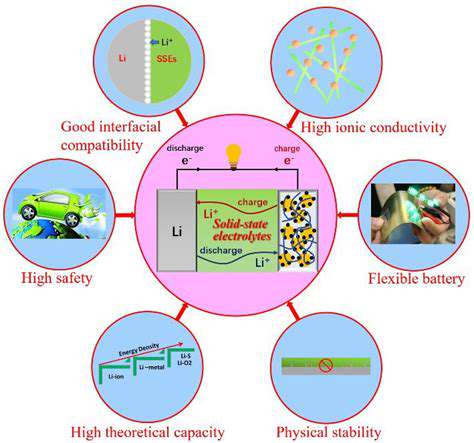
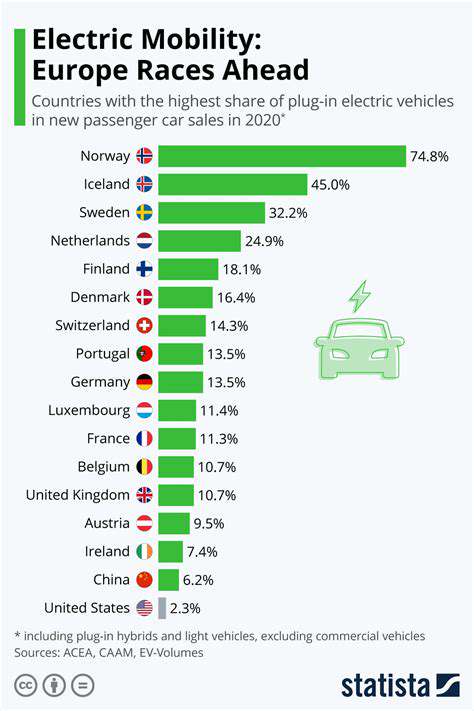
Raw Material Scarcity and Supply Chain Instability

Challenges in Extracting Natural Resources
Obtaining raw materials from the earth's crust frequently encounters substantial ecological hurdles. Mineral extraction operations frequently result in ecosystem degradation, topsoil loss, and groundwater pollution. These consequences can wreak havoc on regional biodiversity and populations dependent on these environments. Implementing eco-conscious methodologies proves essential for reducing harmful outcomes while maintaining ethical resource procurement.
Additionally, the swelling global appetite for natural resources strains conventional extraction techniques beyond capacity. This mounting strain typically coincides with rising operational expenses, creating financial hurdles for corporations - especially when dealing with dwindling supplies of readily available deposits.
Political Tensions and Material Shortages
International conflicts and diplomatic strains frequently interrupt worldwide raw material distribution networks. Such interruptions may trigger deficits and sudden cost surges, harming sectors dependent on these commodities. Nations depending heavily on imported raw materials face particular exposure to these market instabilities. These weaknesses underscore the necessity for broadening procurement strategies and distribution channels.
Civil unrest in resource-abundant territories can create erratic supply chain breakdowns with global industrial consequences. This unpredictability stresses the critical nature of durable supply chain frameworks and multi-origin procurement.
Ecological Policies and Responsible Practices
Rigorous environmental legislation continues transforming how industries obtain and refine raw materials. Corporations confront escalating demands to implement greener operations that lessen ecological harm. Complying with these standards frequently necessitates substantial capital expenditures in novel systems and methodologies. These constraints catalyze inventive solutions and the creation of environmentally preferable options.
Heightened public consciousness regarding ecological degradation from irresponsible practices motivates both governments and businesses to enforce stricter environmental protocols. These mandates compel enterprises to adopt procedures that curb resource waste and emissions, thereby advancing more sustainable material acquisition strategies.
Technological Progress and Creative Solutions
Cutting-edge technological developments significantly enhance both the productivity and environmental compatibility of mineral extraction processes. Emerging innovations demonstrate potential for minimizing the ecological footprint of mining and refinement operations. Such progress proves indispensable for satisfying escalating material needs while curtailing undesirable environmental repercussions.
Revolutionary approaches in extraction and processing technologies address critical challenges posed by shrinking resource stocks. These breakthroughs frequently incorporate novel methods for material reclamation, recycling systems, and waste control measures that collectively boost operational sustainability.
Strengthening Supply Networks
Developing more durable and varied supply networks remains paramount for reducing vulnerabilities tied to material shortages and distribution interruptions. Expanding raw material origins diminishes reliance on singular geographic areas. This expanded procurement approach helps shield industries from cost instability and logistical failures.
Cultivating alternative distribution channels and fortifying partnerships with multiple suppliers proves vital for enduring stability and adaptability. Such strategy demands anticipatory planning that identifies and resolves potential disruptions before operational impacts occur.
Financial Consequences of Shortages
Diminishing raw material availability carries substantial economic implications, influencing product pricing across sectors. These effects permeate diverse industries, affecting enterprises of all scales. Rising costs may constrain consumer expenditure and hinder economic expansion.
Escalating expenses related to material scarcity can precipitate inflationary pressures and diminished consumer buying capacity. Businesses encounter heightened production costs that may erode profitability and potentially affect workforce stability.
Moral Dimensions of Procurement
Ethical material acquisition practices gain mounting significance in contemporary supply chains. Organizations experience intensifying scrutiny to guarantee their distribution networks exclude labor violations and ecological harm. This encompasses maintaining equitable employment standards and conscientious environmental stewardship throughout operational pipelines.
Supply chain openness and responsibility form foundational elements for establishing consumer and investor confidence. This involves disclosing comprehensive data regarding material origins and refinement processes. Modern consumers demonstrate growing awareness of ethical procurement standards and their broader implications, stimulating market preference for transparent and accountable sourcing methods.