Solid-State Batteries: A Revolutionary Leap in Energy Storage
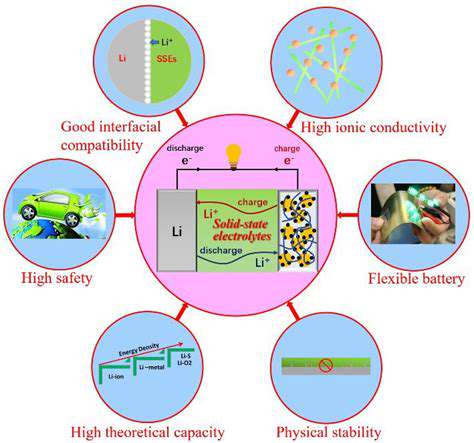
The world of energy storage is on the cusp of transformation with the emergence of solid-state batteries. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries that rely on liquid electrolytes, these advanced power sources employ solid electrolytes. This fundamental shift in design brings about substantial improvements in both performance and safety. The absence of flammable liquids eliminates one of the most significant hazards associated with current battery technology, paving the way for more compact and efficient energy solutions across multiple industries.
For applications where safety is non-negotiable – such as electric vehicles and consumer electronics – this breakthrough couldn't come at a better time. The risk of thermal runaway, a persistent issue with lithium-ion batteries, becomes virtually nonexistent with solid-state designs. Engineers and designers can now explore more aggressive packaging solutions without compromising user safety.
Power Packed Performance
When it comes to energy storage capacity, solid-state technology represents a quantum leap forward. The ability to store more energy in smaller spaces unlocks new possibilities for product design and functionality. Electric vehicles could see dramatic increases in range, while smartphones might finally achieve multi-day battery life without constant recharging.
This density advantage isn't just about size reduction – it's about enabling applications that were previously impossible. From medical implants to aerospace systems, the implications are staggering. The technology effectively redraws the boundaries of what we consider possible in portable power.
Built to Last
Durability stands as another hallmark of solid-state designs. Where traditional batteries degrade noticeably after hundreds of cycles, their solid-state counterparts demonstrate remarkable resilience. This longevity translates to fewer replacements and more reliable performance throughout a device's lifespan.
The economic implications are equally impressive. Longer-lasting batteries mean reduced waste and lower total cost of ownership, benefits that will resonate with both consumers and businesses alike. For industries relying on battery-powered equipment, this reliability could significantly impact operational efficiency.
Faster Power, Quicker Charging
Imagine charging your electric vehicle in the time it takes to grab a coffee. With solid-state technology, this scenario moves from fantasy to impending reality. The unique properties of solid electrolytes facilitate remarkably fast charging without compromising battery health or safety.
This feature alone could revolutionize consumer behavior and infrastructure planning. The psychological barrier of range anxiety that plagues electric vehicle adoption might soon become a relic of the past.
Overcoming Development Hurdles
While the potential is undeniable, significant challenges remain in bringing this technology to mass production. Material scientists continue working to identify optimal electrolyte compositions that balance performance with manufacturability. The path from laboratory success to factory production presents its own set of complex obstacles.
The industry must develop scalable, cost-effective manufacturing processes to make these batteries accessible. Current production methods that work for prototypes often don't translate well to high-volume output. Solving these challenges will require unprecedented collaboration between researchers, engineers, and manufacturers.
A Future Powered Differently
The applications for solid-state batteries read like a roadmap for technological progress. From transforming personal electronics to enabling next-generation renewable energy systems, the possibilities are boundless. The transportation sector alone stands to undergo radical changes as these batteries become commercially viable.
We're not just looking at incremental improvements – this technology represents a fundamental shift in how we store and use energy. As development continues, we may soon witness the dawn of a new era in power storage, with implications that will ripple across every sector of the global economy.