Introduction to Eco-Friendly Practices in Automotive Assembly
Understanding the Urgency of Eco-Friendly Practices
Our planet faces unprecedented environmental challenges that require immediate action. The consequences of climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss are no longer theoretical—they're visible in our daily lives. From extreme weather events to dwindling natural resources, the evidence demands a fundamental shift in how we approach manufacturing and consumption.
Defining Eco-Friendly Practices
Sustainable manufacturing practices focus on reducing environmental harm while maintaining productivity. Key elements include minimizing waste, conserving energy, and prioritizing renewable resources. In automotive assembly, this translates to innovative production methods that maintain quality while protecting ecosystems.
The Impact of Manufacturing Choices
Every production decision creates ripple effects throughout the supply chain. When multiple manufacturers adopt greener practices, the cumulative effect can transform entire industries. Simple changes like optimizing material usage or improving energy efficiency collectively make a substantial difference.
Sustainable Materials and Processes
The shift toward eco-conscious production requires rethinking material selection. Manufacturers now prioritize recycled metals, biodegradable components, and renewable resources. This approach not only reduces environmental impact but often improves product longevity and performance.
Innovative Technologies in Green Manufacturing
Modern factories increasingly incorporate cutting-edge solutions to minimize their ecological footprint. Advanced robotics, AI-driven optimization, and closed-loop water systems demonstrate how technology enables sustainable production. These innovations prove environmental responsibility and industrial efficiency can coexist.
Energy-Conscious Production Facilities
Automotive plants are reimagining their energy infrastructure. By combining renewable energy sources with smart grid technology, facilities achieve both environmental and economic benefits. Solar arrays, wind turbines, and geothermal systems are becoming standard features in forward-thinking factories.
Collaborative Environmental Stewardship
True sustainability requires cooperation across industries and communities. When manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers align around environmental goals, the potential for positive change multiplies. Shared knowledge and coordinated action amplify individual efforts into meaningful progress.
Optimizing Manufacturing Processes for Reduced Waste and Energy Consumption
Streamlining Material Usage
Progressive manufacturers employ precision engineering to minimize material waste. Techniques like computer-aided design and 3D printing allow for exact material placement, dramatically reducing excess. This precision not only conserves resources but also reduces production costs and improves product consistency.
Energy-Efficient Production Systems
Modern assembly lines integrate smart energy management throughout operations. Variable-speed motors, regenerative braking systems, and intelligent lighting networks demonstrate how technology optimizes power usage. These systems automatically adjust to production demands, eliminating unnecessary energy expenditure.
Intelligent Production Scheduling
Advanced planning algorithms now optimize workflow efficiency in real-time. By analyzing multiple variables simultaneously, these systems minimize machine idle time and reduce energy peaks. The result is smoother operations with lower energy consumption and increased throughput.
Responsible Supply Chain Management
Leading manufacturers scrutinize every link in their supply chain for sustainability. Partnering with eco-conscious suppliers ensures materials meet strict environmental standards from source to factory. This comprehensive approach extends a company's green commitment beyond its immediate operations.
Data-Driven Process Improvements
IoT sensors and analytics platforms provide unprecedented visibility into manufacturing efficiency. Real-time monitoring identifies waste streams and energy leaks that traditional methods might miss. This granular data enables targeted improvements with measurable environmental benefits.
Embracing Renewable Energy and Carbon Offsetting in Car Assembly Plants
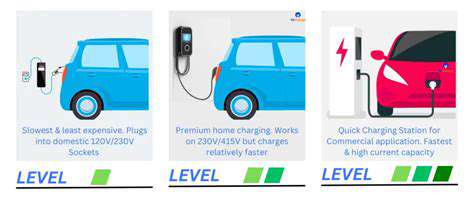
Transitioning to Clean Energy
Forward-thinking automotive plants are investing heavily in on-site renewable generation. Solar canopies over parking lots and wind turbines integrated into campus design demonstrate commitment to sustainable operations. These investments often pay for themselves through long-term energy savings.
Comprehensive Carbon Management
Beyond reducing emissions, progressive manufacturers implement holistic carbon strategies. Verified offset programs combined with direct emission reductions create a balanced approach to climate impact. This dual strategy addresses both immediate and long-term environmental goals.
Closed-Loop Material Systems
Innovative plants are designing production flows that eliminate waste. By treating every byproduct as a potential input for another process, facilities achieve near-zero waste operation. This circular approach mirrors natural ecosystems' efficiency.
Workforce Environmental Engagement
Sustainability succeeds when embraced at all organizational levels. Employee training programs transform factory workers into active participants in environmental stewardship. This cultural shift ensures green practices become ingrained in daily operations.
The Role of Circular Economy Principles in Eco-Friendly Car Assembly
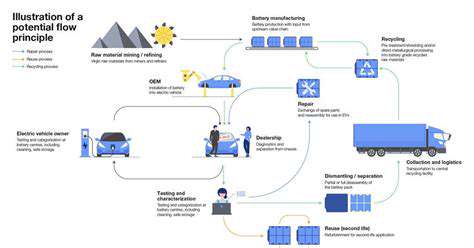
Designing for Product Longevity
Automakers are reengineering vehicles for extended service life. Modular designs allow component replacement rather than whole-vehicle disposal when parts wear out. This approach dramatically reduces material consumption over a vehicle's lifespan.
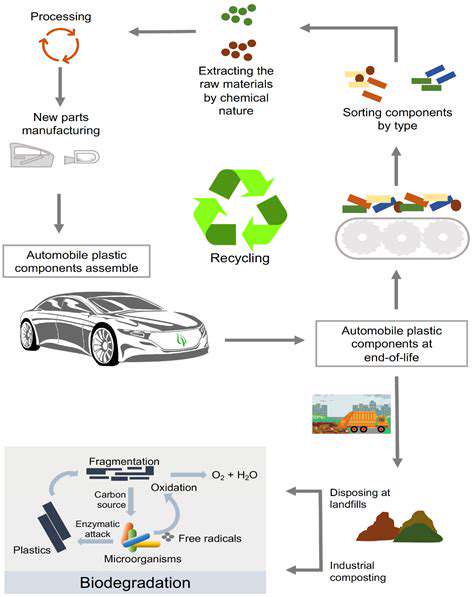
Advanced Recycling Infrastructure
Modern recycling facilities can recover over 90% of a vehicle's materials. Specialized processes separate and purify materials for reuse in new vehicles or other products. This closes the material loop and reduces demand for virgin resources.
New Ownership Models
Innovative business models challenge traditional vehicle ownership. Subscription services and shared mobility options optimize vehicle utilization and extend useful life. These approaches reduce the total number of vehicles needed while maintaining transportation access.
Policy-Driven Sustainability
Governments worldwide are implementing regulations that encourage circular practices. Extended producer responsibility laws motivate manufacturers to design for recyclability from the outset. Such policies align economic incentives with environmental outcomes.