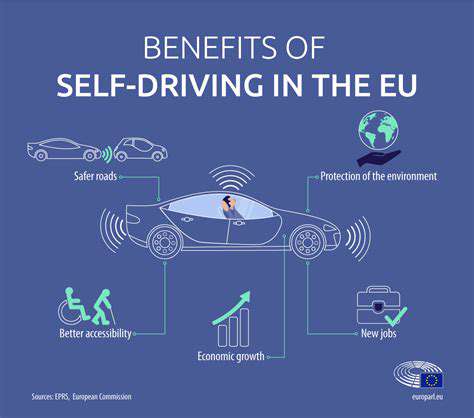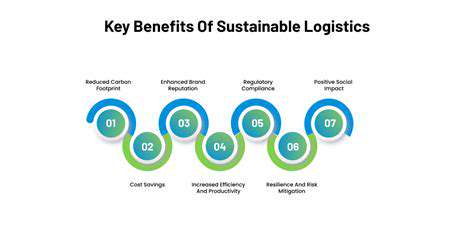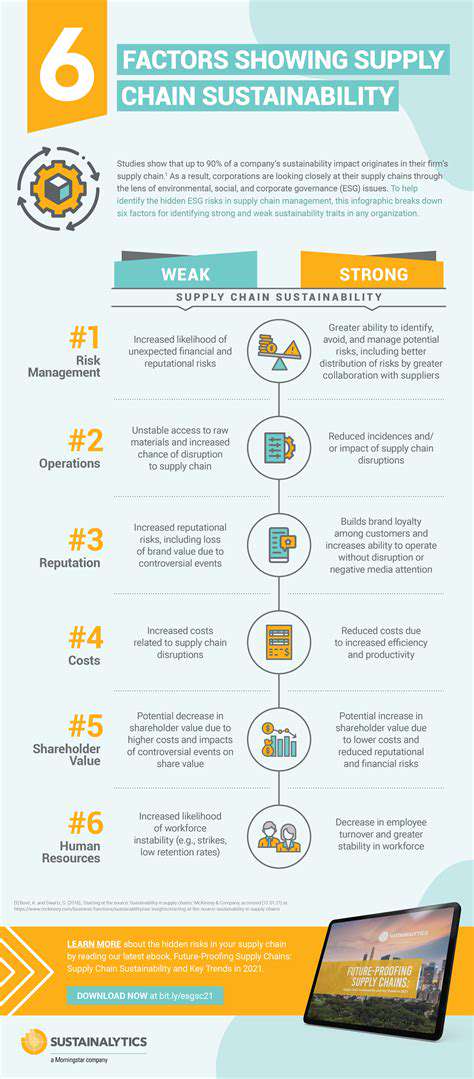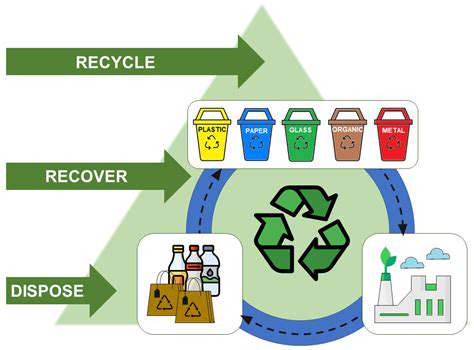
Materials Science Advancements
Material innovation is a critical driver of progress across numerous sectors, from energy production to healthcare. Scientists and engineers are constantly pushing the boundaries of materials science, exploring new properties and functionalities to address global challenges. This exploration encompasses a wide range of approaches, including the development of novel synthesis methods, the manipulation of existing materials at the atomic level, and the creation of entirely new composite materials.
The focus on advanced materials is not simply about improving existing products. It's about fundamentally changing how we design and build everything from automobiles to aerospace components. This advancement often leads to significant performance improvements, including increased strength, durability, and efficiency.
Sustainable Material Solutions
A significant aspect of material innovation is the growing focus on sustainability. Developing materials that are environmentally friendly throughout their lifecycle, from extraction and processing to disposal, is paramount. This includes exploring bio-based materials, recycled content, and materials with reduced carbon footprints. Such efforts are essential for mitigating the environmental impact of manufacturing and consumption.
The transition towards circular economies is heavily reliant on the development of sustainable materials, allowing for the reuse and recycling of resources. The push for more sustainable practices is also driving the need for materials that can be easily recycled and repurposed, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
Applications in Emerging Technologies
Material innovation is directly intertwined with the advancement of emerging technologies, such as renewable energy and advanced computing. New materials are essential for optimizing energy storage, improving solar panel efficiency, and enabling faster and more efficient microchips. These applications demand materials with unique properties, such as high conductivity, flexibility, or strength.
The development of advanced sensors, actuators, and other components for smart systems also relies heavily on material innovation. These technologies require materials with specific functionalities, enabling the integration of advanced sensing and control capabilities into a wide range of applications.
Future Directions and Challenges
The future of material innovation promises exciting advancements, but also presents considerable challenges. Forecasting the specific breakthroughs and their impact on society is difficult, but the potential for revolutionizing various sectors, such as transportation, construction, and medicine, is immense.
A major challenge lies in the scalability and cost-effectiveness of new material production methods. Developing sustainable and efficient processes for large-scale manufacturing will be crucial for widespread adoption. Furthermore, ensuring the safety and environmental compatibility of new materials throughout their entire lifecycle is also of utmost importance.
Lean Manufacturing and Waste Reduction Strategies

Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing, a systematic approach to eliminating waste and maximizing value, is rooted in the principles of continuous improvement. This philosophy emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and designing processes that efficiently meet those needs while minimizing resources consumed. By focusing on eliminating non-value-added activities, lean manufacturing seeks to create a more efficient and responsive production system. The core concept revolves around identifying and eliminating waste in all forms, from unnecessary inventory to excess motion, thereby improving overall productivity and profitability.
Identifying and Eliminating Waste
A crucial component of lean manufacturing is the identification and elimination of waste, often referred to as muda. This includes various forms of waste, such as overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, overprocessing, and defects. Understanding the specific types of waste within a particular process is vital for implementing effective solutions. Waste analysis tools and techniques help pinpoint these areas, allowing for targeted improvements and streamlined workflows.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a powerful lean tool that visually represents the flow of materials and information within a process. It helps to identify bottlenecks, delays, and areas of non-value-added activities. By mapping the entire value stream, from raw materials to the finished product, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the process and pinpoint opportunities for improvement. This visualization process is crucial for effective waste elimination and efficiency gains.
Employee Empowerment and Teamwork
Lean manufacturing emphasizes the importance of employee empowerment and teamwork. Engaging employees in the improvement process fosters a culture of continuous improvement and problem-solving. Empowering employees to identify and suggest solutions to process inefficiencies can significantly enhance the effectiveness of lean initiatives. Empowering employees with the knowledge and authority to make changes, coupled with a collaborative environment, leads to more efficient and effective solutions.
5S Methodology
The 5S methodology, a cornerstone of lean manufacturing, focuses on organizing the workplace for efficiency and effectiveness. The five steps – Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain – aim to create a clean, organized, and safe work environment. Implementing 5S principles reduces waste by improving workflow, minimizing errors, and enhancing overall productivity. By establishing a well-organized and clean work environment, employees can focus on their tasks with a greater sense of efficiency and clarity. This methodology can significantly streamline operations and enhance overall quality control.
Measuring and Monitoring Results
To ensure the effectiveness of lean manufacturing initiatives, it is essential to establish clear metrics and regularly monitor progress. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead time, cycle time, defect rates, and inventory levels provide valuable insights into the impact of implemented changes. Continuous monitoring and analysis of these metrics allow for adjustments and further improvements in the process. Regularly tracking and evaluating the results of implemented strategies is critical for success. Through data-driven analysis, adjustments can be made to maximize the impact of lean initiatives.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Integration

Energy Efficiency Strategies for Homes
Implementing energy efficiency strategies in homes is crucial for reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills. Proper insulation significantly reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, leading to substantial energy savings. This can be achieved through various methods, such as installing insulation in walls, attics, and basements. High-performance windows and doors also play a critical role in improving energy efficiency. These measures not only save money but also contribute to a more comfortable living environment.
Choosing energy-efficient appliances is another key aspect of home energy efficiency. Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate their high energy-efficiency performance. Replacing older, less efficient models with newer, more energy-efficient ones can yield substantial long-term savings. By adopting these practices, homeowners can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainable living.
Renewable Energy Sources
Harnessing renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable future. Solar power, utilizing sunlight to generate electricity, is a prominent renewable energy source. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Wind energy, leveraging the kinetic energy of wind, is another significant renewable energy source. Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity, providing a reliable and clean power source. Both solar and wind energy technologies are rapidly advancing, becoming increasingly cost-effective and efficient.
Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives and policies play a crucial role in promoting energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption. Tax credits and rebates for energy-efficient upgrades can significantly reduce the upfront costs for homeowners. These incentives encourage greater adoption of sustainable practices, driving the transition toward a cleaner energy future.
Public awareness campaigns and educational programs are also important initiatives. These programs educate consumers about the benefits of energy efficiency and renewable energy, fostering a greater understanding and promoting widespread adoption.
Economic Benefits of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency measures offer significant economic benefits for businesses and homeowners. Reducing energy consumption directly lowers utility bills, leading to substantial cost savings over time. This translates to greater profitability for businesses and increased disposable income for households.
Furthermore, investments in energy efficiency can lead to increased property values. Homes and businesses that prioritize energy efficiency are often perceived as more attractive and valuable assets.
Environmental Impact of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels. Renewable energy technologies produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, mitigating the negative effects of climate change.
The reduced reliance on fossil fuels translates to a cleaner environment and healthier air quality. Promoting renewable energy is crucial for mitigating the detrimental effects of climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.
Technological Advancements in Energy
Technological advancements are constantly improving energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies. Innovations in solar panel design, for example, are increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Similarly, advancements in wind turbine technology are enhancing power generation capabilities and reducing environmental impact.
These ongoing advancements are paving the way for a more sustainable energy future, offering promising solutions for a cleaner and more efficient energy sector.