Driving the Future of Energy: Understanding Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
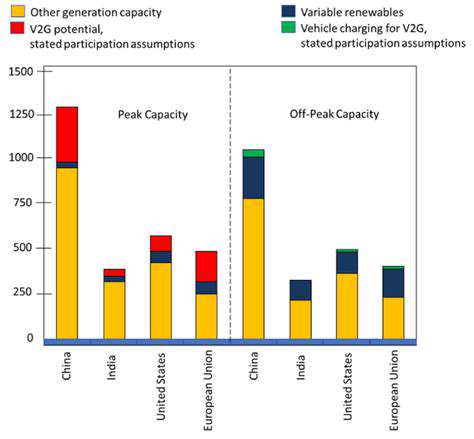
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is a revolutionary concept that promises to reshape the way we generate and consume electricity, paving the way for a more sustainable future. It essentially allows electric vehicles (EVs) to act as mobile power sources, feeding electricity back into the grid during periods of high demand or low generation. This innovative approach presents a compelling solution to address the challenges associated with intermittent renewable energy sources and the fluctuating energy demands of modern society. By harnessing the stored energy in EV batteries, V2G systems can provide crucial support to the grid infrastructure.
The potential for V2G to enhance grid stability is significant. Imagine a scenario where a sudden surge in energy demand occurs, perhaps due to a power outage or increased industrial activity. V2G technology can then deploy the stored energy in connected EVs to compensate for this fluctuation, thereby ensuring the grid's reliability and preventing blackouts. This capability is particularly valuable in regions heavily reliant on renewable energy sources, which often exhibit unpredictable power output.
Unlocking the Potential of V2G: Benefits and Challenges
Beyond grid stability, V2G technology offers a host of other advantages. It can contribute to a more efficient energy distribution system, potentially reducing the need for new power plants and lowering energy costs for consumers in the long run. Furthermore, the integration of V2G with smart grids allows for real-time adjustments to energy flow, optimizing overall energy management and promoting energy independence.
However, the widespread adoption of V2G technology faces several challenges. One key hurdle is the development of standardized communication protocols and charging infrastructure. Ensuring compatibility between different V2G systems and creating a robust charging network that supports bidirectional energy flow is crucial for widespread deployment. Another significant challenge lies in the cost of implementing V2G technology for both EVs and the grid infrastructure. Reducing the upfront costs and providing attractive incentives for EV owners are essential for the technology to achieve widespread adoption.
Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits of V2G are undeniable. As the technology matures and the associated challenges are addressed, V2G is poised to become a critical component of a sustainable energy future. The transition to a more electrified transportation sector, coupled with the integration of V2G, could significantly reduce carbon emissions and pave the way for a cleaner, more resilient energy system.
Challenges and Considerations

Economic Factors
Economic downturns can significantly impact the success of a project, requiring careful consideration of potential budget constraints and the availability of funding. Project managers need to develop contingency plans to address unexpected financial fluctuations. This might involve exploring alternative funding sources or adjusting project timelines and scopes to align with available resources. Economic instability can also affect market demand, potentially impacting the project's overall viability.
Analyzing the current economic climate and its potential impact on the project's financial projections is crucial. Understanding the potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them will be key to project success in an uncertain economic environment.
Technical Challenges
Technical limitations and complexities can arise during the execution of a project. Implementing new technologies or integrating with existing systems might present unforeseen difficulties, requiring adjustments to project plans. Unexpected technical issues can be costly and time-consuming to resolve, potentially delaying the project's completion.
Thorough technical assessments at the outset of a project can help identify potential obstacles. Planning for potential technical roadblocks and having a robust troubleshooting strategy in place can minimize the impact of unforeseen issues.
Resource Management
Effective resource management is essential for project success. This includes securing the necessary personnel, equipment, and materials on time. Delays in securing resources can significantly impact project timelines and potentially increase project costs. Managing resource availability and allocation effectively is crucial to maintaining a smooth workflow and preventing bottlenecks.
Proper communication and collaboration among team members are critical to ensure that resources are utilized effectively. Clear communication and well-defined roles and responsibilities will minimize conflicts and ensure that everyone understands their tasks and deadlines.
Stakeholder Management
Managing stakeholder expectations and maintaining positive relationships is vital for a project's success. Misunderstandings or conflicts with stakeholders can derail a project, leading to delays, cost overruns, and even project cancellation. Actively engaging with stakeholders and addressing their concerns promptly can prevent these potential issues.
Regular communication, transparency, and a proactive approach to addressing stakeholder concerns will help build trust and foster collaboration. This will contribute to a positive project environment and ultimately improve the chances of successful project completion.
External Factors
External factors, such as regulatory changes, political instability, or natural disasters, can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. Projects operating in dynamic environments need to be prepared for unforeseen events that could alter the project's course. Contingency plans for these external factors are necessary to minimize the negative impact on the project.
Monitoring external factors and their potential impact on the project is crucial. Regular risk assessments and proactive adaptation to changing conditions will be essential to successfully navigate external challenges. This proactive approach is key to minimizing disruptions and maximizing project success.