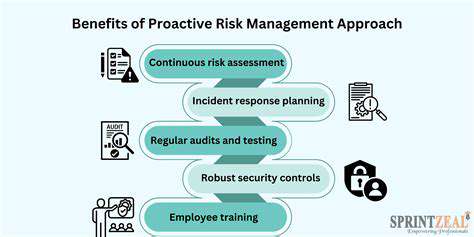
The Trade-offs and Challenges of EGR Systems
The Economic Implications
The shift towards a globalized economy, driven by advancements in technology and transportation, has undeniably led to increased trade and economic interdependence. This interconnectedness, while fostering opportunities for growth and prosperity, presents a multitude of economic trade-offs. For example, the pursuit of lower production costs often leads to job displacement in developed countries, prompting complex discussions about the social safety nets needed to mitigate these negative consequences. Furthermore, the uneven distribution of benefits from globalization can exacerbate existing inequalities and create social tensions. This necessitates a careful consideration of policies that promote equitable economic growth and sustainable development. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the complexities of global trade and ensuring that its benefits are shared broadly.
A significant challenge lies in managing the volatility inherent in global markets. Fluctuations in exchange rates, commodity prices, and interest rates can create considerable uncertainty for businesses and consumers alike. This instability can disrupt supply chains, leading to economic hardship. Additionally, the interconnected nature of global markets means that shocks in one region can quickly ripple through the entire system. Effective international cooperation and coordination are essential to mitigate these risks and promote financial stability. The need for robust regulatory frameworks to manage these economic forces is paramount for long-term prosperity.
The Societal and Environmental Considerations
The expansion of global trade has profound societal consequences, impacting everything from cultural exchange to labor standards. Increased interaction between nations fosters cultural exchange and understanding, but it can also lead to the erosion of traditional values and cultural identities. The spread of ideas and products, while often positive, can also contribute to homogenization and a loss of diversity. It's vital to strike a balance between embracing globalization's benefits and preserving cultural heritage.
Environmental concerns are inextricably linked to global trade. The transportation of goods across vast distances contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the pursuit of cheap production often leads to exploitative labor practices and environmental degradation in developing countries. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort to promote sustainable practices throughout the supply chain and to ensure that the benefits of trade are not achieved at the expense of the environment. International cooperation is crucial for developing and implementing effective environmental regulations that minimize the negative impact of trade on global ecosystems.
Another key societal challenge is the impact of trade on labor standards. The drive to lower production costs can sometimes lead to exploitative labor practices, including low wages, unsafe working conditions, and the suppression of worker rights. Developing and enforcing global labor standards that protect workers' rights and ensure fair treatment is crucial to fostering a more equitable and sustainable global economy. Furthermore, the potential for job displacement in developed nations necessitates robust social safety nets to protect vulnerable populations and ensure a smooth transition to new economic opportunities.