What is a Push-Button Start System?
Understanding the Basics
Modern vehicles increasingly adopt push-button start systems, replacing the traditional key ignition. Instead of fumbling with keys, drivers enjoy the simplicity of pressing a button to fire up the engine. This innovation doesn't just offer convenience—it represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with our vehicles. The system's electronic architecture manages everything from driver authentication to engine activation, creating a seamless start-up experience that feels distinctly contemporary.
At its core, the technology relies on sophisticated electronic controls that communicate with various vehicle systems. These controls verify authorization through encrypted signals, ensuring only approved users can operate the vehicle. The system's intelligence extends beyond mere ignition, often integrating with other vehicle functions for enhanced performance and security.
Key Components of a Push-Button Start System
The system's operation depends on several critical components working in harmony. The most visible element is undoubtedly the starter button itself—a sleek interface that belies the complexity beneath. However, the real magic happens through a network of sensors and antennas that detect authorized key fobs within the vehicle's interior. This invisible handshake between vehicle and key represents a significant advancement in automotive security technology.
Vehicle computers have evolved into sophisticated gatekeepers, processing authentication data while simultaneously managing multiple vehicle systems. These computers don't just enable engine start—they coordinate with dashboard displays, safety systems, and even climate controls to create a fully integrated driving experience from the moment of ignition.
Benefits of Using a Push-Button Start System
The advantages extend far beyond the obvious convenience factor. By eliminating physical keys, these systems dramatically reduce opportunities for traditional hot-wiring techniques, making vehicles significantly harder to steal. The precision of electronic ignition also contributes to fuel efficiency, as the system can optimize start-up sequences based on engine temperature and other variables.
Modern drivers appreciate how these systems complement other technologies like remote start—a welcome feature during extreme weather. The absence of a traditional ignition cylinder also allows for more creative interior designs, giving automakers greater freedom to create visually appealing and ergonomic cockpit layouts.
Security Features and Safety Considerations
Contemporary push-button systems employ multiple layers of security. Advanced encryption protocols between key fobs and vehicle computers create a formidable barrier against unauthorized access. Many systems incorporate motion sensors that deactivate the fob when stationary, preventing relay attacks that exploit signal amplification techniques.
Safety remains paramount with any ignition system, and manufacturers build in multiple fail-safes. These include automatic engine shutdown if no driver presence is detected, backup manual start procedures, and clear dashboard indicators that show the vehicle's operational status. Understanding these features helps drivers use the technology safely and effectively.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
While generally reliable, push-button systems benefit from basic maintenance. Keeping the starter button area clean prevents debris interference, while regular battery checks for both vehicle and key fob ensure consistent operation. The system's electronics typically require minimal attention, but benefit from occasional professional diagnostics during routine service.
When issues arise—such as intermittent starting problems—professional diagnosis proves essential. Modern systems generate detailed trouble codes that trained technicians can interpret, often revealing simple solutions like fob battery replacement or more complex electrical issues requiring specialized attention.
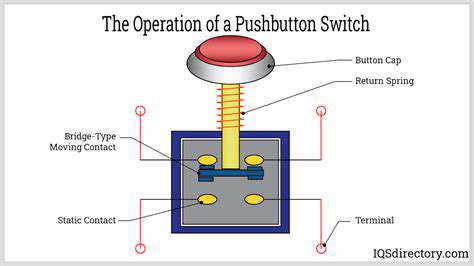
Key Components of a Keyless Ignition System

Ignition System Overview
Keyless technology revolutionizes how we start vehicles by replacing mechanical keys with smart authentication. Modern systems may incorporate various access methods including proximity sensors, smartphone apps, or biometric verification. This flexibility allows manufacturers to create unique brand experiences while maintaining robust security standards.
The fundamental purpose remains unchanged—initiating combustion—but the execution achieves new levels of sophistication. Digital authentication protocols not only prevent theft but also enable innovative features like personalized driver settings that activate upon engine start.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
As the system's neural center, the modern ECU handles far more than just ignition. These powerful computers continuously monitor dozens of vehicle parameters while executing complex authentication protocols. Their processing power enables real-time adjustments that optimize everything from fuel delivery to emissions control based on driving conditions.
Advanced ECUs even learn driver habits over time, subtly adjusting various systems to match individual preferences. This adaptive capability represents a significant leap from traditional fixed-parameter engine management.
Transponder Key or Key Fob
Today's smart keys have evolved into sophisticated devices with multiple functions. Many incorporate motion sensing, touch-sensitive controls, and even small displays showing vehicle status. The underlying security technology has similarly advanced, with rolling encryption codes that change with each use to prevent code grabbing attacks.
Immobilizer System
Modern immobilizers represent one of auto theft prevention's greatest success stories. These systems combine physical and digital security layers that work together to create a formidable anti-theft barrier. Some systems now incorporate GPS and cellular connectivity, allowing vehicle tracking and remote immobilization if theft occurs.
The technology continues advancing with features like biometric verification and multi-factor authentication becoming more common in premium vehicles.
Sensors and Actuators
The sensor network in contemporary vehicles creates a detailed real-time picture of both vehicle and environment. These systems monitor everything from seat occupancy to ambient light levels, feeding data to the ECU for processing. This sensor fusion enables intelligent features like automatic engine shutdown if the driver exits the vehicle.
Actuators have similarly evolved, with electronic throttle control and smart starter motors that adjust their operation based on engine conditions for smoother, more reliable starts.
User Interface and Control
Interface design plays a crucial role in system adoption. Successful implementations balance security with convenience, offering intuitive controls that feel natural to use. Many systems now incorporate voice commands, smartphone integration, and even gesture controls. This focus on user experience transforms what was once a simple mechanical action into an engaging technological interaction.
The best systems become nearly invisible in operation—reliable enough that drivers take their function for granted while offering enough flexibility to accommodate different usage scenarios and preferences.