Optimizing Battery Production Processes
The production of modern EV batteries requires careful attention to energy use at every step. From obtaining raw materials to assembling battery cells, keeping energy use low is essential. Using lean manufacturing methods, like just-in-time inventory systems, helps cut down on energy wasted during material handling and storage. Advanced technologies such as automation and robotics can make production lines more efficient, reducing mistakes and energy used for repetitive tasks. Keeping precise temperature control throughout the facility is also key, as it can greatly lower energy consumption during battery production.
Creative process design is vital for energy efficiency. This means looking into alternative methods that use less energy. For example, using solar or wind power to run the facility can reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency. Choosing energy-saving equipment and machinery for every stage, from material processing to final quality checks, leads to significant energy conservation.
Minimizing Waste Generation
A major part of sustainable EV battery manufacturing is reducing waste at every step. This requires a complete approach that includes careful material selection, efficient production techniques, and strong waste management. Closed-loop recycling systems for recovered materials allow valuable resources to be reused, cutting down on the need for new materials and lessening environmental harm. Strict quality checks at each stage can catch defects early, reducing waste. Proper waste separation and treatment are also crucial for handling hazardous materials.
Waste reduction goes beyond the production floor. A thorough waste audit program can find areas for improvement, identify waste sources, and develop targeted solutions. By examining the type and amount of waste produced, manufacturers can reduce hazardous waste disposal, lowering environmental and health risks. Encouraging employees to focus on waste reduction fosters shared responsibility and innovative solutions.
Implementing Sustainable Materials
Using sustainable and recycled materials is key to making EV battery manufacturing more environmentally friendly. Exploring materials with lower environmental impact during sourcing is essential. For example, using recycled lithium, nickel, and cobalt can greatly reduce the environmental impact of obtaining these resources. This approach not only eases the strain on natural resources but also cuts the energy needed to extract and process new materials. Recycled materials can also lower production costs while improving environmental performance.
Researching bio-based materials for manufacturing is another way to boost sustainability. Replacing traditional components with bio-based alternatives can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and support a circular economy. This reduces the environmental impact of manufacturing and creates a more sustainable supply chain. Ongoing research is needed to test the effectiveness of these materials in real-world applications.
Advanced Recycling and Reuse Strategies
Developing strong recycling and reuse methods for old EV batteries is crucial for a sustainable manufacturing cycle. Advanced recycling technologies that recover valuable materials from used batteries are essential. Innovative chemical and physical processes can separate and recover metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt. These materials can then be reused in new batteries, creating a closed-loop system and reducing the need for new resources. This approach not only lessens environmental impact but also saves costs over time.
Building a solid recycling infrastructure is key to making these strategies work. This includes partnering with recycling facilities, creating standard recycling methods, and ensuring safe handling of hazardous materials. Public awareness campaigns can also encourage responsible battery disposal and recycling. A reliable recycling system ensures a sustainable future for EV battery technology.
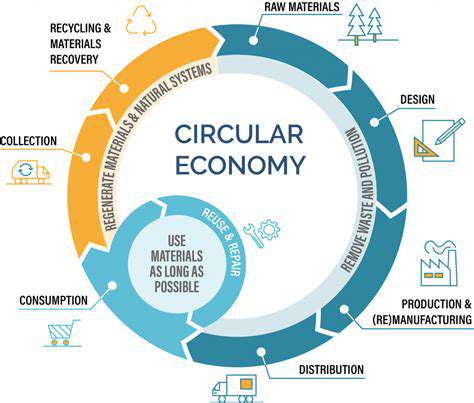
Recycling and Reuse: A Circular Economy Approach
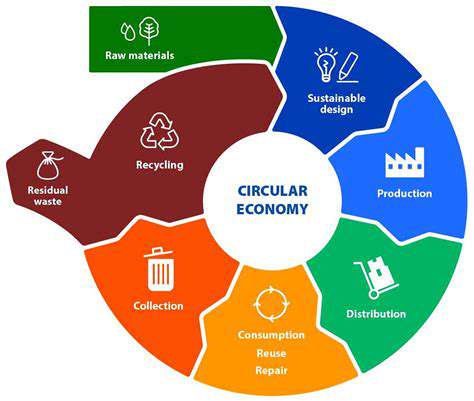
Recycling: A Foundation for Sustainability
Recycling plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of consumption. By keeping waste out of landfills, we save resources and ease the strain on ecosystems. Recycling reduces the need to extract raw materials, protecting natural habitats and cutting pollution from mining and processing. This complex process is essential for a sustainable future.
Recycling covers many materials, from paper and plastic to glass and metal. Each material needs specific methods to ensure recycled products maintain quality and can be reused. This careful process supports continuous resource use, minimizing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Reuse: Extending the Lifespan of Products
Reuse means finding new purposes for items that would otherwise be thrown away. This extends product life, reducing demand for new materials and cutting waste. Repurposing old items can be a rewarding and cost-effective alternative to buying new products.
From turning old jars into storage containers to upcycling clothes into accessories, reuse offers many possibilities. Encouraging a culture of reuse can significantly lower environmental impact and promote sustainable consumption.
The Economic Benefits of Recycling and Reuse
Recycling and reuse create jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing, boosting economic growth. They also cut costs tied to waste management and resource extraction, making them viable for businesses and communities.
These programs reduce the need for new raw materials, lowering reliance on imports and strengthening local economies. This eases the burden on waste disposal infrastructure, saving money for governments.
Environmental Impacts of Not Recycling and Reusing
Failing to recycle and reuse has serious consequences. Landfills overflow, releasing harmful gases and polluting soil and water. Extracting raw materials causes deforestation, habitat loss, and pollution.
Making new products from virgin materials uses vast energy and resources. Embracing recycling and reuse can reduce these impacts and build a sustainable future.
The Importance of Consumer Awareness
Consumer awareness is key to successful recycling and reuse. People need to understand proper waste separation and local recycling options. This knowledge helps them make sustainable choices.
Teaching consumers about recycling and reuse benefits encourages participation. This can greatly reduce waste and create a more environmentally aware society.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies drive recycling and reuse. Effective rules can encourage businesses and individuals to adopt sustainable practices. Strong waste disposal regulations and recycling incentives can transform waste management.
Policies promoting reusable and recyclable product design push manufacturers to include these features. Such measures are vital for a circular economy and a sustainable future.
Community Engagement and Collaboration
Community involvement is essential for effective recycling and reuse. Local groups can run awareness campaigns, workshops, and education programs. Partnerships between businesses, governments, and communities amplify these efforts.
Building a sense of shared responsibility fosters sustainability and environmental care. Collaborative actions can significantly cut waste and promote sustainable living.
Policy and Collaboration: Fostering Sustainable Innovation

Policy Framework
A strong policy framework is key to successful collaboration. It should define roles, responsibilities, and expectations clearly. Clear communication and dispute resolution guidelines are essential. This structure ensures consistent action and alignment with goals.
Policies should also cover sensitive information handling and data privacy. These protocols build trust and create a collaborative environment where people feel safe sharing information.
Collaboration Protocols
Effective collaboration needs clear protocols for communication, sharing, and decision-making. These protocols must be easy to access and regularly updated. This includes setting communication channels, project timelines, and conflict resolution processes.
Standardized documentation of decisions and actions is also important. This transparency helps with future reference and improvement.
Communication Strategies
Open and honest communication builds trust and collaboration. A clear communication plan should outline methods, frequency, and channels for updates. Use emails, project tools, and meetings to keep everyone informed.
Active listening and constructive feedback are crucial. Encouraging open dialogue makes everyone feel valued and heard.
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms
Disagreements are inevitable in collaboration. A proactive approach to conflict resolution prevents disruptions. A structured process for addressing conflicts fairly keeps the atmosphere positive and productive.
Training team members in conflict resolution helps them handle disagreements constructively, maintaining collaboration.
Stakeholder Engagement
Successful collaboration requires engaging all stakeholders. Understanding their needs and views ensures the project meets their expectations. Seeking input and feedback at every stage is crucial.
Resource Management
Efficient resource management is vital for collaboration. This includes identifying, allocating, and tracking resources to meet project deadlines and budgets. Clear roles and responsibilities for resource management are essential for success. Proper allocation and tracking keep projects on schedule.
Clear processes for requesting, approving, and tracking resources streamline collaboration.
Evaluation and Improvement
Regular evaluation and feedback drive continuous improvement. This means assessing policies, protocols, and strategies. Gathering stakeholder feedback and analyzing data helps identify areas for improvement.
Making changes based on evaluations strengthens collaboration and ensures future success.