Beyond the Realm of Simple Mistakes
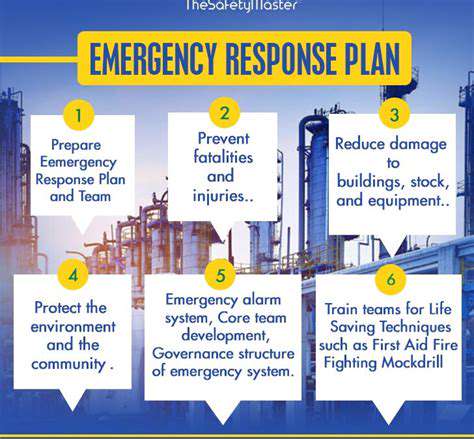
Human error, while a significant factor in safety incidents, often masks deeper systemic issues. Examining safety protocols and procedures is crucial to understanding and mitigating the risks that lie beyond individual mistakes. A comprehensive approach to safety must delve into the root causes of incidents, not just the immediate actions that led to them. This proactive approach allows for the identification and rectification of flawed systems and processes, fostering a safer and more reliable environment.
Addressing the underlying vulnerabilities within a system is far more impactful than solely focusing on individual training or disciplinary measures. A deeper dive into the design, implementation, and maintenance of safety measures is essential. This broader perspective is vital to creating a truly robust safety culture.
Technological Advancements in Safety Protocols
Modern technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing safety protocols. From real-time monitoring systems to predictive maintenance algorithms, these advancements are transforming how we approach risk management. Advanced sensors and data analytics can provide invaluable insights into potential hazards, enabling proactive interventions and reducing the likelihood of incidents.
Implementing sophisticated safety systems, like automated shut-off mechanisms or emergency response protocols, can significantly enhance safety measures in high-risk environments. These systems can act as a critical safeguard, minimizing the impact of human error and preventing catastrophic failures.
Proactive Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Proactive risk assessment is paramount in preventing incidents before they occur. This involves a thorough analysis of potential hazards, considering various factors, including environmental conditions, operational procedures, and potential human error. Identifying and evaluating these risks is crucial for developing targeted mitigation strategies.
Developing and implementing robust mitigation strategies that address the identified risks is essential. These strategies should incorporate a variety of solutions, from procedural changes to the installation of safety equipment. By proactively addressing potential problems, organizations can create a safer working environment for everyone.
Cultivating a Safety-Conscious Culture
A strong safety culture is not just about implementing policies and procedures; it's about fostering a mindset where safety is prioritized and valued by everyone involved. This involves ongoing training, communication, and engagement to ensure that safety remains a top concern across all levels of the organization.
Promoting open communication channels and encouraging employees to report near misses or safety concerns is vital. Creating a culture where everyone feels comfortable voicing their concerns and contributing to a safer environment is crucial for long-term success.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations: Ensuring Reliability and Public Trust
Addressing Systemic Issues
Ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of any system, especially one with public implications, requires a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities. This includes a comprehensive analysis of the system's architecture, design, and implementation, looking for potential weaknesses or points of failure. Rigorous testing at various stages, from unit to integration and system testing, can help uncover hidden flaws and ensure the robustness of the system in various scenarios.
Furthermore, the process of ongoing maintenance and updates is critical. Systems are not static; they evolve and adapt to new demands and challenges. Regular updates, bug fixes, and security patches are essential to maintain reliability and protect against emerging threats. This ongoing commitment to improvement is paramount to building public trust and ensuring the long-term viability of the system.
Mitigating Bias and Ensuring Fairness
Systems, especially those used for critical decision-making, need to be carefully evaluated for potential biases. These biases can stem from the data used to train the system, the algorithms themselves, or even the developers' inherent perspectives. Addressing these biases requires rigorous scrutiny of the data sources, the algorithms employed, and the development process itself.
Implementing mechanisms to detect and mitigate bias is crucial. This involves developing metrics to assess the fairness and equity of the system's outputs and incorporating procedures to address identified biases. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the system's performance in diverse contexts is essential to ensure that it treats all individuals fairly and equitably, thus building public trust.
Maintaining Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in the design, development, and operation of the system is fundamental to fostering public trust. Clear documentation of the system's architecture, algorithms, and decision-making processes should be readily available to stakeholders, allowing them to understand how the system functions and why it makes specific decisions. This transparency builds accountability, as stakeholders can evaluate the system's performance and identify potential issues or areas for improvement.
Establishing clear lines of accountability is also vital. Defining roles and responsibilities for different parties involved in the system's lifecycle ensures that there are mechanisms in place to address complaints, rectify errors, and take corrective actions when necessary. This accountability framework enhances public trust by demonstrating a commitment to responsible development and operation of the system.
Managing User Expectations and Providing Support
Clearly defined and realistic expectations are crucial to the success of any system. Educating the public about the system's capabilities and limitations, as well as providing clear instructions and support materials, can help manage user expectations and avoid potential frustrations or misunderstandings. Thorough documentation and user-friendly interfaces are vital to ensuring that users can effectively interact with the system.
Providing comprehensive support channels, such as FAQs, help centers, and dedicated customer service, is paramount to addressing user concerns and resolving issues promptly. Effective support mechanisms demonstrate a commitment to user satisfaction and can significantly contribute to positive public perception and trust in the system.
The Impact on Future Infrastructure and Regulations: Shaping a Safer Future
Infrastructure Adaptation for a Changing World
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, driven by climate change, necessitate a fundamental shift in infrastructure design and construction. Traditional approaches, often optimized for historical weather patterns, are no longer sufficient. We need infrastructure that is resilient, adaptable, and capable of withstanding more severe conditions. This includes upgrades to water management systems, the development of flood-resistant buildings, and the reinforcement of critical infrastructure like bridges and power grids to ensure continued function during extreme events. This adaptation will require significant investment and a commitment to long-term planning, considering the potential impact on various sectors of society.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies into infrastructure is crucial for proactive monitoring and response. Real-time data collection on weather patterns, infrastructure stress levels, and potential risks will allow for quicker and more effective interventions. This proactive approach to infrastructure management will not only enhance safety but also optimize resource allocation and minimize economic losses from disruptions.
Regulatory Frameworks to Foster Safety
Current regulatory frameworks need to be re-evaluated and strengthened to reflect the evolving risks and challenges posed by climate change. Outdated building codes and safety standards may no longer adequately protect against the intensified weather events. New regulations must incorporate climate-change projections into design guidelines, mandating the use of more resilient materials and construction methods. This necessitates collaboration among government agencies, industry stakeholders, and researchers to ensure comprehensive and effective regulations that promote safety and resilience in the face of a changing climate.
Beyond building codes, new regulations should address the broader societal impacts of extreme weather events. This includes strategies for community preparedness, evacuation plans, and the development of early warning systems. By proactively considering the potential impacts of extreme weather events, regulations can reduce vulnerability and enhance the overall safety and well-being of communities. Moreover, regulations must address the equity aspects of infrastructure improvements, ensuring that vulnerable populations are not disproportionately affected by the changing climate.
Effective and timely enforcement of these new regulations is equally important. Clear guidelines, consistent application, and appropriate penalties for non-compliance will be essential to ensuring that the safety standards are adhered to and that the improved infrastructure is effectively utilized. This will require ongoing monitoring, adaptation, and refinement of the regulatory frameworks to keep pace with the evolving climate risks.
In conclusion, the future of infrastructure must be shaped by a forward-thinking approach that integrates resilience and adaptability into every aspect of design, construction, and operation. Simultaneously, robust and adaptable regulations will be vital in ensuring that the infrastructure is not only built to withstand severe weather events but also addresses the broader societal implications of these events.