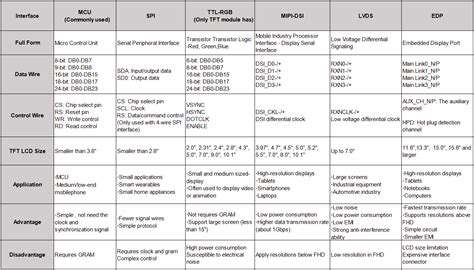
Emerging Roles in the Autonomous Driving Ecosystem
Software Engineers
Building and maintaining self-driving car systems demands top-tier software engineering talent. These professionals craft the complex algorithms enabling vehicles to perceive environments, make split-second decisions, and navigate roads safely. Their work combines expertise in computer vision, machine learning, and AI with rigorous software development practices. The dynamic nature of autonomous technology means engineers must constantly refine models, incorporate new data streams, and solve novel challenges that emerge during real-world operation.
Data Scientists
The brains behind autonomous vehicles rely on massive datasets, and data scientists serve as the vital link between raw information and functional intelligence. They process billions of data points from cameras, radar, and GPS to train machine learning models that power vehicle perception and decision-making. Beyond technical skills, these specialists ensure data quality and representativeness, which directly impacts system reliability. Their validation processes help guarantee vehicles can handle diverse driving scenarios safely.
Safety Engineers
Public acceptance of autonomous vehicles hinges on demonstrated safety, creating critical roles for safety specialists. These professionals design comprehensive testing protocols, develop fail-safe mechanisms, and analyze potential failure modes. Collaborating across teams, they identify system vulnerabilities and implement solutions that maintain safety standards. Their work blends engineering rigor with deep understanding of traffic dynamics and human factors to create robust safety frameworks.
Cybersecurity Specialists
As connected vehicles become rolling computers, cybersecurity experts stand as the first line of defense against digital threats. They architect security systems to protect vehicle networks, software, and communication channels from malicious actors. Their work prevents potentially catastrophic scenarios where hackers could compromise vehicle control systems. Ongoing threat assessment and rapid response protocols ensure autonomous fleets remain secure as attack vectors evolve.
Transportation Planners and Policy Makers
The autonomous revolution requires fundamental changes to transportation infrastructure and regulations. Urban planners and policymakers face the challenge of integrating self-driving vehicles into existing road networks while addressing equity concerns. They must develop new frameworks for liability, insurance, and traffic management that account for mixed autonomous and human-driven environments. Their decisions will shape how cities leverage autonomous technology to improve mobility while minimizing disruption.
The Need for Adaptability and Upskilling
The Changing Landscape of Transportation
Self-driving technology promises to transform mobility, affecting everything from daily commutes to global supply chains. Urban centers must reconsider road designs, parking infrastructure, and public transit networks to accommodate autonomous fleets. This transition requires unprecedented collaboration between technologists, planners, and policymakers to create seamless integration strategies.
The shift extends beyond physical infrastructure to operational models. Ride-sharing services may transition to fully autonomous fleets, while delivery networks could become more efficient through coordinated autonomous logistics. These changes demand flexible thinking and willingness to reinvent established transportation paradigms.
Reskilling for a Future with Autonomous Vehicles
The automation of driving tasks will inevitably displace some transportation jobs, particularly in commercial trucking and taxi services. However, this disruption creates opportunities for workers to transition into emerging technical roles. Effective reskilling programs should focus on areas like AI system maintenance, fleet operations management, and data analysis - skills that will be in high demand.
Community colleges and vocational schools are already developing curricula to prepare workers for these new positions. Successful programs combine hands-on technical training with foundational knowledge about autonomous systems, creating pathways for career transitions.
The Impact on Urban Design and Infrastructure
City planners face both challenges and opportunities as autonomous vehicles become prevalent. Dedicated lanes for self-driving cars, dynamic traffic signal systems, and redesigned intersections could dramatically improve traffic flow. Parking infrastructure may transform as autonomous vehicles can drop passengers and park remotely.
These changes require careful planning to ensure equitable access and prevent unintended consequences like increased urban sprawl. Pilot programs in various cities are testing different approaches to integration, providing valuable data for broader implementation.
Economic Implications and Opportunities
The autonomous vehicle revolution presents a complex economic picture. While certain driving jobs may decline, new opportunities will emerge in vehicle maintenance, software development, and mobility services. The potential efficiency gains could reduce transportation costs by 40-60%, benefiting businesses and consumers alike.
Policymakers must address potential inequality in these economic shifts, ensuring workforce transition programs and creating frameworks that distribute benefits broadly. The technology could also stimulate new business models in last-mile delivery, mobility-as-a-service, and urban logistics.
Ethical Considerations and Public Safety
Autonomous systems raise profound ethical questions about decision-making in critical situations. Consensus must be reached on how vehicles prioritize safety in unavoidable accident scenarios. Transparent testing protocols and clear liability frameworks will be essential for building public trust.
Ongoing monitoring systems and over-the-air updates allow continuous safety improvements. Regulatory agencies are developing certification processes to ensure autonomous vehicles meet rigorous safety standards before deployment.
The Future of Personal Mobility
Self-driving technology could dramatically expand mobility options for underserved populations. Elderly individuals and people with disabilities may gain unprecedented independence through autonomous transportation. Urban residents might rely less on personal car ownership as on-demand autonomous services become ubiquitous.
This shift could transform urban landscapes, reducing parking needs and allowing repurposing of urban space. However, careful planning is needed to ensure these benefits are distributed equitably across socioeconomic groups.
Navigating Ethical and Legal Implications: New Responsibilities

Navigating the Complexities of Ethical Considerations
Ethical frameworks become crucial guides as autonomous systems make life-impacting decisions. Developers must balance competing priorities like safety, privacy, and algorithmic fairness when programming vehicle behaviors. Multidisciplinary ethics boards are emerging to provide guidance on these complex issues, drawing from philosophy, law, and engineering perspectives.
Transparency in decision-making processes helps build public trust. Some companies are publishing their ethical guidelines and decision-making frameworks to demonstrate their commitment to responsible development.
Assessing Potential Legal Ramifications
The legal landscape for autonomous vehicles remains in flux as legislators grapple with novel scenarios. Clear liability frameworks must distinguish between manufacturer responsibility and owner/operator obligations. Insurance models are evolving to account for these new risk profiles, with some proposals favoring no-fault systems for autonomous vehicle incidents.
International harmonization of regulations will be important as autonomous vehicles cross borders. Standardized safety certifications and operational guidelines can facilitate global deployment while maintaining high safety standards.
Developing Robust Compliance Strategies
Automakers and tech companies are establishing comprehensive compliance programs to navigate evolving regulations. These include internal audit processes, documentation standards, and whistleblower protections. Effective compliance requires continuous monitoring of regulatory developments across all jurisdictions where vehicles may operate.
Some companies are creating dedicated regulatory affairs teams that work closely with engineering groups to ensure systems are designed with compliance in mind from the outset.
Maintaining Transparency and Accountability
Data transparency is becoming a key differentiator in the autonomous vehicle sector. Many companies now publish regular safety reports detailing testing mileage, disengagement statistics, and incident reports. This openness helps regulators and the public assess progress while holding developers accountable.
Some jurisdictions are implementing requirements for data recorders in autonomous vehicles, similar to airplane black boxes, to facilitate incident investigation and system improvement.
Prioritizing Stakeholder Interests
The autonomous vehicle ecosystem involves numerous stakeholders with sometimes competing interests. Manufacturers must balance innovation with safety, while cities seek to integrate the technology without disrupting existing transit systems. Inclusive stakeholder engagement processes help identify concerns early and build consensus around deployment strategies.
Public forums, industry working groups, and regulatory advisory committees provide channels for diverse voices to shape the development of autonomous transportation systems.
Adapting to Evolving Standards
The regulatory environment for autonomous vehicles changes rapidly as technology advances. Companies must build agile compliance structures that can adapt to new requirements. Participation in standards development organizations helps shape future regulations while keeping abreast of emerging expectations.
Forward-looking organizations are investing in regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions to automate aspects of compliance monitoring and reporting as requirements multiply.
The Future Workforce: A Multifaceted Landscape
Autonomous Vehicles and the Reshaping of Transportation
The workforce transformation accompanying autonomous vehicles will be both disruptive and creative. While traditional driving roles may decline, entirely new categories of employment will emerge. Fleet managers for autonomous vehicles, remote operation specialists, and mobility service designers represent just a few of the novel positions taking shape.
This transition requires proactive workforce development strategies. Partnerships between industry and educational institutions are creating pathways for workers to transition into these new roles through targeted training programs.
The Impact on Existing Job Roles
Commercial drivers facing automation can transition into related roles such as fleet technicians, safety operators, or logistics coordinators. The human element remains important even in autonomous systems, particularly for oversight, customer service, and exception handling.
Training programs that combine technical skills with industry-specific knowledge can facilitate these transitions. Some companies are creating internal academies to retrain existing employees for new positions within the autonomous vehicle ecosystem.
Emerging Job Roles and Skill Requirements
The autonomous vehicle revolution is creating demand for specialists in several key areas:
- AI trainers who develop and refine machine learning models using real-world driving data
- Simulation engineers who create virtual environments for testing autonomous systems
- Teleoperation specialists who remotely assist vehicles in complex situations
- Mobility service designers who create user experiences for autonomous transportation
These roles require combinations of technical expertise, creative problem-solving, and human-centered design thinking.
The integration of autonomous vehicles into society will be an ongoing process requiring adaptability from both workers and organizations. Companies that invest in continuous learning and skills development will be best positioned to navigate this transformation successfully.