Planning and Design Considerations
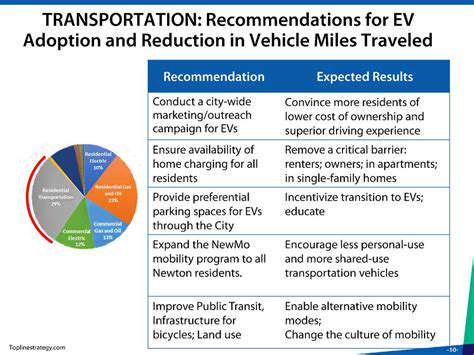
Implementing charging infrastructure in apartment buildings requires careful planning to ensure both the practicality and efficiency of the system. A key initial step is a thorough assessment of the building's electrical system capacity and potential limitations. This includes evaluating the existing wiring, circuit breakers, and overall power distribution to determine if the current setup can support the increased load of electric vehicle charging stations. Understanding the projected number of EV owners and the expected charging demand is crucial for sizing the charging infrastructure appropriately. Failing to account for these factors can lead to significant problems down the line, such as circuit overload or insufficient power availability, impacting the charging experience for residents and potentially causing safety hazards.
Another critical aspect of planning involves the design and placement of charging stations. Strategic placement is essential to maximize accessibility and minimize congestion. Factors to consider include proximity to parking spaces, accessibility for residents with disabilities, and potential interference with other building amenities. The design should also prioritize ease of use and user-friendliness, including clear signage, intuitive interfaces, and convenient payment systems. This user-centric approach will encourage adoption and ensure a positive experience for EV owners.
Financial and Regulatory Aspects
The financial implications of implementing charging infrastructure in an apartment building are significant and must be carefully considered. Calculating the upfront costs, including the purchase and installation of charging stations, associated permits, and any necessary upgrades to the electrical system, is essential for budgeting purposes. Long-term operational costs, such as maintenance, repairs, and potential energy consumption increases, should also be factored into the overall financial plan. Exploring potential funding options, such as grants, loans, or resident contributions, may help alleviate some of the financial burden.
Navigating the regulatory landscape is also crucial. Understanding local building codes, electrical safety regulations, and any specific requirements for EV charging stations in the area is paramount. Complying with these regulations ensures the safety and legality of the installation and minimizes potential risks or penalties. Consulting with qualified professionals, such as electricians and legal experts, is highly recommended to ensure a seamless and compliant installation process.
Incentives for residents, such as reduced parking fees for EV owners, or potential rebates for installing the system, can help promote the adoption of EVs and encourage participation in the charging infrastructure project. Careful consideration of these incentives can significantly impact the project's success and feasibility, making it more attractive and sustainable for both the building management and residents.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of these financial and regulatory factors is essential for the successful implementation of charging infrastructure.
Furthermore, understanding the potential environmental benefits and long-term cost savings associated with EV adoption is crucial when making this investment.
Battery capacity degradation is a natural process that affects all rechargeable batteries over time. This gradual decline in the battery's ability to store and deliver power is primarily driven by chemical changes within the battery's internal components. Understanding this process is critical for predicting battery lifespan and optimizing its use. The rate of degradation varies depending on several factors, including the battery chemistry, environmental conditions, and usage patterns.