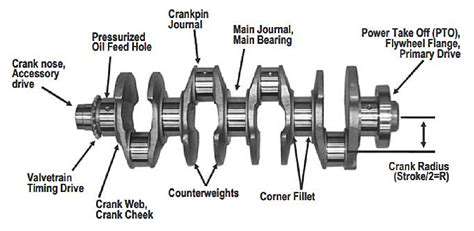
Pinpointing and Removing Waste
A fundamental aspect involves relentlessly hunting down and eradicating waste. Here, waste doesn't just mean scrap material - it encompasses any action that fails to enhance the end product's worth. Examples range from needless employee movements to piled-up components or workflow congestion. Through exhaustive examination of each production phase, organizations can detect improvement opportunities and implement targeted fixes.
Many businesses employ detailed process mapping techniques to visualize inefficiencies clearly. Value Stream Mapping has become particularly popular for highlighting problem zones and developing enhancement strategies.
Enhancing Process Flow
Perfecting how work progresses forms the backbone of lean implementation. This means optimizing how parts and information travel through the entire manufacturing sequence. Creating seamless, uninterrupted workflows enables firms to slash production durations, boost manufacturing volumes, and react swiftly to shifting market needs.
Achieving this frequently demands radical changes to traditional factory layouts, workspace reorganizations, and improved interdepartmental communication protocols.
Workforce Engagement Strategies
Lean methodologies place tremendous value on employee involvement and cooperative problem-solving. Frontline workers possess invaluable insights, making their participation critical for identifying and resolving operational challenges. This philosophy fosters greater job ownership and motivation, resulting in more dedicated teams. By tapping into staff knowledge regularly, companies unlock creative solutions that drive efficiency.
Regular team meetings and structured feedback systems help maintain this collaborative environment where improvement suggestions flow freely.
The Kaizen Mindset
Lean represents an ongoing evolution rather than a final destination. It demands persistent learning, adaptation, and refinement. This philosophy of perpetual betterment pushes organizations to constantly seek superior methods for delivering value. The objective isn't just maintaining standards but consistently surpassing them through innovative thinking.
Tracking key metrics, gathering stakeholder input, and adjusting methods based on new information all support this continuous improvement cycle.
Advantages of Lean Adoption
Embracing lean principles delivers multifaceted benefits that extend well beyond financial savings. These include higher output rates, compressed production schedules, better quality outputs, happier customers, and more energized teams. By relentlessly attacking waste and perfecting processes, businesses achieve unprecedented operational excellence and financial performance. Additionally, the ingrained improvement culture fosters innovation that helps companies adapt to market shifts.
Such streamlined systems demonstrate remarkable flexibility when facing demand fluctuations or evolving customer requirements, ensuring lasting market relevance.
Eco-Conscious Manufacturing Through Lean Principles
Smarter Resource Management
Lean and sustainability initiatives share common ground in optimal resource utilization. While lean targets all forms of waste, green practices emphasize conservation and ethical sourcing. Combining these approaches helps manufacturers shrink their environmental impact while boosting efficiency - a win-win scenario that cuts expenses, improves profits, and strengthens brand perception among eco-aware consumers.
Detailed analysis of material streams, production sequences, and energy usage reveals optimization opportunities. These insights guide strategies for waste reduction, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable material selection. Applying lean thinking to supply chain operations further minimizes environmental damage from sourcing and logistics activities.
Waste Minimization Techniques
The lean focus on eliminating waste aligns perfectly with ecological goals, since waste generation directly affects the environment. Streamlined production not only enhances operational performance but also dramatically reduces ecological footprints. Practical examples include material-saving cutting methods, energy-efficient equipment upgrades, and optimized transportation networks - all contributing to greener, leaner operations.
Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Sustainability advocates champion circular economy models where materials circulate continuously through reuse and recycling. Lean methodologies support this vision through designs emphasizing repairability and recyclability. Such approaches minimize waste generation and maximize component reuse, easing pressure on natural resources and reducing landfill contributions.
Greening the Supply Network
True sustainability requires complete supply chain visibility. Lean tools enhance transparency and tracking capabilities. By simplifying supply networks and partnering with like-minded vendors, manufacturers can reduce transportation emissions and ensure ethical material sourcing. This cooperative model cuts logistics costs, accelerates deliveries, and maintains sustainability standards across all supply tiers.
Cultivating Green Awareness
Merging sustainability with lean operations necessitates organizational mindset shifts. Success depends on workforce engagement through comprehensive training programs covering resource efficiency, waste reduction tactics, and responsible procurement importance. Well-informed employees become sustainability champions who drive meaningful change.
The Dual Advantage
The lean-sustainability combination delivers powerful financial and environmental returns. Lean methods drive down costs and boost productivity, while green practices enhance corporate image and reduce ecological harm. Together, they create resilient businesses that prosper financially while protecting our planet.
Lean Manufacturing's Automotive Evolution

Digital Transformation of Lean
Traditional lean principles are converging with advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT systems. This fusion enhances traditional waste reduction and process optimization approaches, granting manufacturers unprecedented responsiveness in volatile markets. The breakthrough comes from data-powered insights that illuminate operational realities with crystal clarity. Real-time performance metrics enable precise bottleneck identification and process refinements, replacing guesswork with empirical decision-making.
Automation's Growing Role
Smart automation technologies - from self-navigating vehicles to sophisticated robotics - are redefining production workflows. These innovations minimize human error while dramatically improving output consistency. However, successful integration requires careful workforce planning. Companies must invest heavily in employee retraining, transitioning staff from manual tasks to roles supervising and optimizing automated systems.
Green Lean Manufacturing
Tomorrow's lean factories will prioritize environmental responsibility alongside efficiency. This means energy-efficient operations, waste minimization, and material recycling systems. Sustainable lean practices offer dual benefits - they're both ecologically sound and financially prudent. Reduced resource consumption lowers costs while meeting regulatory requirements and appealing to green-minded customers. Forward-thinking manufacturers are adopting renewable energy, carbon reduction strategies, and environmentally-friendly processes to ensure long-term viability.
These developments point toward an exciting future where lean principles evolve through digital innovation and environmental stewardship, maintaining their relevance in tomorrow's automotive industry.