Financial Incentives and Public-Private Partnerships

Financial Incentives for Public-Private Partnerships
Financial incentives play a crucial role in attracting private sector participation in public-private partnerships (PPPs). These incentives can take many forms, including tax breaks, subsidies, and grants. Incentives are designed to offset some of the perceived risks associated with PPPs, making them more attractive to potential private partners. A well-structured incentive program can significantly improve the likelihood of successful project completion and implementation.
Careful consideration must be given to the design and implementation of these incentives to ensure they are effective and equitable. This includes assessing the potential impact on public finances and ensuring that the incentives are aligned with broader public policy goals. Clearly defined terms and conditions are essential for transparency and accountability.
Types of Financial Incentives
Various financial incentives can be deployed to encourage private sector involvement in PPPs. These include tax credits, subsidies for specific investments, and grant funding for research and development related to the project.
Subsidies can be provided for infrastructure development or the operation of public services, effectively reducing the financial burden on the private partner. Additionally, the provision of favorable loan terms and guarantees can also act as powerful financial incentives.
Risk Mitigation through Incentives
PPPs often involve a degree of risk for both public and private sectors. Financial incentives can act as a crucial risk mitigation strategy, making the project more appealing to private investors. This is especially true in projects with high upfront costs or uncertain future revenues.
By reducing the perceived risk, incentives can encourage more private sector participation and potentially lead to lower overall project costs. This is because private companies often have access to more efficient and cost-effective methods of project execution.
Public-Private Partnerships and Public Funding
Public funding, often in the form of grants or subsidies, is vital for bridging the gap between the public sector's needs and the private sector's investment requirements. These funds can be allocated for various aspects of the project, including initial capital investments, operational costs, or research and development.
The allocation of public funds must be transparent and based on clear criteria to ensure fairness and accountability in the PPP process. Rigorous due diligence and thorough evaluation of project proposals are essential to ensure that public funds are utilized effectively.
Long-Term Sustainability and Incentives
Incentives should be designed with long-term sustainability in mind. Ensuring the project remains financially viable over its entire life cycle is crucial for both public and private partners. This requires careful consideration of future costs, revenues, and potential changes in the market environment.
Long-term incentives can include performance-based payments or revenue-sharing agreements. These mechanisms can align the interests of both parties and encourage responsible project management and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, flexibility in the incentive structure should be considered to adapt to changing circumstances.
Transparency and Accountability in Incentive Programs
Transparency and accountability are essential components of any successful incentive program for PPPs. Clear and readily accessible information about the incentives, eligibility criteria, and project details is crucial for fostering trust and ensuring fairness. Regular monitoring and evaluation of the program are necessary to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
Establishing clear reporting mechanisms and conducting independent audits can enhance transparency and promote accountability. Furthermore, a robust grievance redressal mechanism should be in place to handle any complaints or disputes arising from the incentive program.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact Considerations
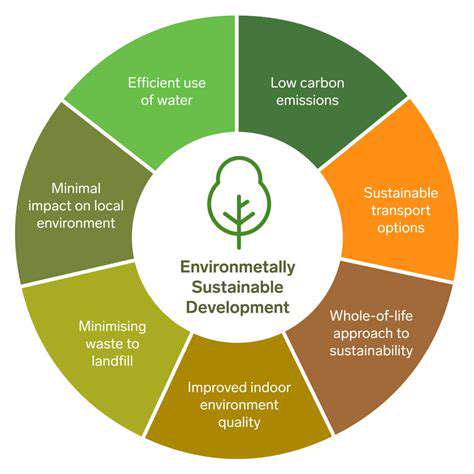
Sustainable Practices in Agriculture
Sustainable agricultural practices are crucial for ensuring long-term food security and minimizing environmental damage. These practices focus on minimizing the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers, promoting biodiversity in farmlands, and adopting water-efficient irrigation techniques. Implementing these practices can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture and promote the health of ecosystems. This approach also often leads to more resilient farming systems that can withstand the impacts of climate change.
By adopting sustainable agricultural methods, farmers can contribute to the conservation of soil health, reduce water pollution, and support biodiversity. These practices also enhance the long-term productivity of agricultural lands, ensuring a sustainable food supply for future generations. Furthermore, sustainable agriculture often fosters a more harmonious relationship between farmers and the environment.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are crucial tools for evaluating the potential effects of development projects on the surrounding environment. They help identify and mitigate potential negative impacts, promoting sustainable development. By analyzing the project's potential consequences, EIAs allow for informed decision-making, balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
A thorough EIA process considers a wide range of factors, such as air and water quality, biodiversity, and habitat disruption. This process often involves public participation, enabling stakeholders to voice their concerns and contribute to the decision-making process. Ultimately, comprehensive EIAs can help guide projects toward a more sustainable future.
Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, offer clean and sustainable alternatives to traditional energy production methods. Harnessing these resources can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a healthier planet.
Investing in renewable energy infrastructure creates new job opportunities and fosters economic growth. Moreover, the transition to renewable energy sources contributes to energy independence and reduces our vulnerability to volatile fossil fuel markets. These sources are crucial for building a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Waste Management and Recycling
Effective waste management and recycling programs are vital for minimizing environmental pollution and resource depletion. These programs aim to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, recover valuable resources, and promote a circular economy. By diverting waste from landfills, we conserve valuable land resources and reduce the environmental burden associated with waste disposal.
Proper waste management practices also contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Recycling materials conserves natural resources, reduces the need for extracting raw materials, and lowers energy consumption associated with manufacturing new products. Implementing comprehensive waste management strategies is essential for a sustainable future.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are critical for safeguarding biodiversity and preserving natural habitats. These efforts involve protecting endangered species, restoring degraded ecosystems, and promoting sustainable use of natural resources. Protecting biodiversity is essential for maintaining the ecological balance of our planet and ensuring the survival of countless species.
Conservation efforts also protect essential ecosystem services, such as clean water, pollination, and climate regulation. These services are crucial for human well-being and contribute significantly to our quality of life. Sustainable conservation practices are vital for ensuring a healthy planet for future generations.
Sustainable Transportation
Promoting sustainable transportation options is crucial for reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This includes encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking. These options reduce reliance on private vehicles, leading to cleaner air and a lower carbon footprint.
Investing in sustainable transportation infrastructure, such as electric vehicle charging stations and dedicated bike lanes, can incentivize the adoption of more environmentally friendly modes of transport. Promoting sustainable transportation is vital for creating healthier and more livable communities, while also mitigating the negative impacts of transportation on the environment.