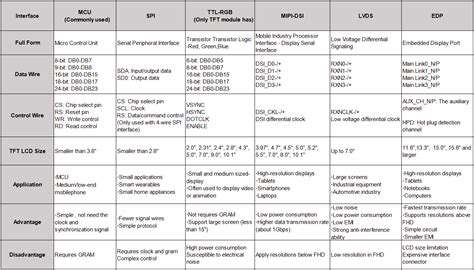
Understanding Diagnostic Codes
Diagnostic codes, often used in healthcare settings, are standardized alphanumeric representations of diseases, injuries, or other medical conditions. These codes are crucial for tracking patient information, analyzing trends, and allocating resources effectively within healthcare systems. They provide a common language that healthcare professionals can use to communicate about patients' conditions across different settings and institutions.
Understanding these codes is essential for navigating the complexities of patient care and ensuring that appropriate treatment plans are developed and implemented. They also play a vital role in research, enabling researchers to identify patterns and trends in disease prevalence and severity, ultimately contributing to advancements in medical knowledge and improved patient outcomes.
Categorization and Classification
Diagnostic codes are organized into various categories and classifications systems, such as the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. These systems categorize conditions based on similar characteristics, anatomical locations, or other relevant criteria, enabling efficient organization and retrieval of patient data.
Categorization and classification ensure consistency and standardization in healthcare data collection and analysis. This standardized approach allows healthcare professionals and researchers to compare data across different populations and time periods, facilitating the identification of trends and patterns in disease prevalence and treatment effectiveness.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The International Classification of Diseases, or ICD, is a widely used diagnostic coding system. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), ICD provides a global standard for diagnosing and classifying diseases. It covers a broad range of medical conditions, from common illnesses to rare diseases, and is essential for epidemiological studies and international comparisons of health data. It is constantly updated to reflect advancements in medical knowledge and evolving disease patterns.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
CPT codes, developed by the American Medical Association (AMA), are used to describe medical procedures, services, and supplies. These codes are critical for billing and reimbursement in healthcare settings. They provide a structured way to document the procedures performed on patients and ensure accurate billing for services rendered. CPT codes are essential for administrative purposes, enabling efficient tracking and documentation of procedures.
Coding in Different Healthcare Settings
Diagnostic codes are used across various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and physician offices. They are employed in electronic health records (EHRs) to record patient diagnoses, facilitating efficient information sharing and analysis among healthcare providers. This streamlined approach ensures that patients receive coordinated and comprehensive care.
Impact on Healthcare Research
Diagnostic codes play a pivotal role in healthcare research, providing researchers with a standardized framework for data analysis. Researchers can use these codes to identify trends in disease prevalence, treatment effectiveness, and patient outcomes. This detailed analysis allows for the development of evidence-based guidelines and protocols, leading to improvements in patient care.
Using these codes allows researchers to focus on the relevant data and draw meaningful conclusions that can significantly impact healthcare practices. This data analysis is crucial in identifying areas where improvements are needed and informing the development of new treatments and preventive measures.
Accuracy and Reliability
Accurate and reliable coding practices are essential for the validity of healthcare data. Inaccurate coding can lead to misleading results in research studies and misallocation of resources. Maintaining high standards in coding practices is critical for the credibility of healthcare data and the effective implementation of public health strategies. Proper training and protocols are essential to ensure that codes are applied consistently and accurately.
Gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, are rapidly transforming biotechnology. These powerful tools allow scientists to precisely target and modify DNA sequences within organisms, opening up exciting possibilities for treating genetic diseases, enhancing agricultural yields, and even developing new biofuels. This revolutionary approach promises to reshape our understanding of biology and medicine. The implications extend far beyond the laboratory, impacting various sectors from healthcare to agriculture, with potential to address critical global challenges.
Using Remote Diagnostics for Preventative Maintenance

Remote Diagnostics: A Powerful Tool for Troubleshooting
Remote diagnostics are rapidly becoming an essential component of modern IT support and maintenance. This innovative approach allows technicians to identify and resolve issues with computer systems and networks from a remote location, saving valuable time and resources. By leveraging advanced technologies, remote diagnostics can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall operational efficiency. This ability to pinpoint problems quickly and effectively is particularly crucial in today's interconnected world.
The benefits of remote diagnostics extend beyond the immediate resolution of problems. Continuous monitoring and proactive intervention make it possible to address potential issues before they escalate into major disruptions. This preventative approach is invaluable in maintaining optimal system performance and minimizing the risk of significant data loss.
Key Technologies Enabling Remote Diagnostics
Several technologies are crucial to the functionality of remote diagnostics. These include robust network connections, secure communication protocols, and sophisticated diagnostic software. Reliable, high-bandwidth internet connections are essential for transferring data quickly and efficiently between the technician and the remote system. This enables prompt identification and resolution of problems without extensive delays.
Advanced software programs often include automated tools for analyzing system logs, identifying hardware errors, and diagnosing network connectivity issues. These features empower technicians with the ability to quickly isolate problems and develop tailored solutions.
Security Considerations in Remote Diagnostics
While remote diagnostics offer numerous advantages, robust security measures are paramount. Protecting sensitive data and maintaining system integrity is of utmost importance when accessing and interacting with remote systems. Stringent security protocols, such as encryption and authentication, must be implemented to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
The use of secure protocols like HTTPS and VPNs is critical for encrypting communication channels. This ensures that all transmitted data remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
The Future of Remote Diagnostics
The future of remote diagnostics is bright, with ongoing advancements promising even greater efficiency and effectiveness. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into diagnostic tools will likely lead to even faster problem identification and resolution. The possibilities for automation and predictive maintenance are vast, leading to significant improvements in IT operations.
Expect to see remote diagnostics becoming even more integrated into everyday IT practices, providing proactive support and reducing the need for on-site intervention in many situations. This evolution will likely include more sophisticated tools for analyzing complex system interactions and predicting potential failures.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility of Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics are often more cost-effective than traditional on-site support. By reducing travel time and expenses, organizations can save significant amounts of money while maintaining high levels of system availability. The ability to quickly resolve problems remotely translates directly into increased productivity and reduced downtime costs.
Furthermore, remote diagnostics can be accessed from anywhere with a reliable internet connection, making it a highly accessible and flexible solution for businesses of all sizes. This accessibility is especially beneficial for geographically dispersed teams or organizations with limited on-site technical personnel.