Understanding the Spectrum of Liability
Accidents, by their very nature, often present complex legal and ethical dilemmas. Determining responsibility isn't always straightforward, as it requires examining multiple contributing elements, from personal oversight to organizational shortcomings. The concepts of strict liability, vicarious liability, and contributory negligence form the foundation for analyzing accident cases. Each situation demands careful scrutiny of its unique circumstances to establish proper accountability.
The Role of Negligence in Determining Accountability
At the heart of accident liability lies the principle of negligence. This legal standard requires proving that a party had a duty of care, failed to meet that duty, and directly caused harm through their failure. Establishing negligence relies on demonstrating actions or inactions that fell below what a prudent person would do in similar conditions. Investigators typically gather expert opinions, witness statements, and comprehensive documentation of the event sequence.
However, assessing negligence becomes particularly challenging when multiple parties share potential responsibility. Determining precise causation often necessitates painstaking reconstruction of events and analysis of all possible contributing factors.
Beyond Individual Actions: Systemic Failures and Liability
Accident causation frequently extends beyond individual mistakes to include institutional shortcomings. Deficient safety measures, equipment malfunctions, or infrastructure deterioration can all play significant roles. When systemic issues contribute to accidents, investigations must broaden to examine corporate policies, industry norms, and regulatory adherence, rather than focusing solely on individual conduct.
The Ethical Implications of Liability Determination
Assigning responsibility for accidents carries profound ethical considerations. The process must prioritize impartiality, justice, and factual accuracy to properly address the harm caused. Potential biases, prejudices, or conflicts of interest must be identified and addressed to maintain the legal process's integrity. These ethical obligations apply equally to all involved parties, from affected individuals to potentially responsible organizations.
Accountability and Compensation for Victims
The fundamental ethical requirement following any accident is ensuring proper accountability for resulting damages. This typically involves providing appropriate restitution to affected parties for their injuries, financial losses, and emotional distress. While monetary compensation cannot reverse what occurred, it serves as crucial recognition of the harm suffered and facilitates some degree of resolution. Determining suitable compensation amounts often involves complex negotiations and emotional considerations.
The Future of Liability and Accountability in Accidents
Evolving technologies and social structures continue to reshape liability frameworks. The growing prevalence of automation, globalized supply chains, and emerging industries introduces novel challenges for legal and ethical standards. Future approaches must account for these changing risk profiles in our interconnected world, developing systems that both prevent incidents and provide fair resolution when they occur. Proactive risk assessment and mitigation will become increasingly critical in this evolving landscape.
Defining Ethical Frameworks for Autonomous Vehicle Decision-Making
Defining Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence
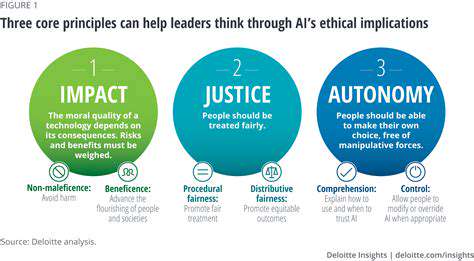
AI systems are transforming numerous sectors, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. This rapid technological advancement demands thorough examination of AI's ethical dimensions. Clear principles must guide development to ensure responsible, equitable deployment that maximizes benefits while minimizing potential harm.
Effective AI governance requires comprehensive ethical frameworks addressing fairness, transparency, responsibility, and data protection. These frameworks must identify and address potential biases in data sources, algorithmic processes, and system design to ensure equitable treatment for all users.
Addressing Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
A primary ethical challenge in AI involves potential biases within algorithms and datasets. When training data reflects societal prejudices, AI systems may reinforce and amplify these biases in their operations. This can result in unjust outcomes that disproportionately affect vulnerable groups. Developers must therefore carefully evaluate training data and implement corrective measures for identified biases.
Achieving algorithmic fairness requires proactive identification and mitigation of biases throughout the development process. This includes utilizing diverse datasets and implementing bias detection techniques. Continuous system monitoring remains essential to prevent the perpetuation of social inequities.
Ensuring Transparency and Explainability in AI
Transparent and understandable AI decision-making processes are fundamental to ethical deployment. Users and stakeholders must comprehend how systems reach conclusions to maintain trust and accountability. Opaque systems make error identification and bias correction difficult, potentially undermining confidence in AI outputs.
Developing interpretable AI systems is crucial for fostering trust and ensuring responsible use. Techniques like explainable AI (XAI) provide visibility into algorithmic decision processes, enabling thorough review and error correction.
Promoting Accountability and Responsibility in AI
Clear accountability structures are necessary to address potential AI-related harms. Determining responsibility when systems fail or cause damage is essential for establishing corrective mechanisms and preventing recurrence.
Establishing definitive responsibility frameworks represents a critical step toward ethical AI development. Such frameworks should clearly delineate roles, obligations, and consequences throughout the AI lifecycle, promoting responsible innovation that benefits society.

Hidden within your vehicle's transmission system lies an often-neglected component that plays a pivotal role in keeping everything running smoothly. This vital fluid not only enables smooth gear transitions but also protects the entire drivetrain from severe damage. Its critical importance frequently becomes apparent only after problems emerge, making regular maintenance absolutely essential.
Addressing the Data Security and Privacy Concerns Associated with Autonomous Vehicles
Data Collection in Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles generate vast quantities of operational data, including location information, speed metrics, environmental conditions, and driver interactions. While essential for system functionality like adaptive cruise control and lane maintenance, this extensive data collection raises substantial privacy issues. Understanding collection protocols, storage practices, and usage parameters is vital for maintaining public confidence and addressing security vulnerabilities.
The constant monitoring of vehicle surroundings creates detailed records of movements and interactions. Without proper safeguards, this information could be exploited for purposes beyond its intended use, creating potential privacy violations and security risks.
Data Storage and Security
Protecting the substantial datasets generated by autonomous vehicles requires robust security measures. Advanced encryption and secure storage facilities are essential to prevent unauthorized access and data compromise. The sensitive nature of collected information demands rigorous protection against both internal and external security threats.
The possibility of malicious actors exploiting system vulnerabilities to access sensitive data or manipulate vehicle controls represents a significant security concern. Implementing comprehensive protective measures is essential for data integrity and system security.
Privacy Implications for Passengers and Drivers
Autonomous vehicles collect extensive personal data about occupants, including travel patterns, behavioral information, and potential health indicators. The possible misuse of this information raises serious privacy concerns that require clear regulatory guidance and ethical usage standards.
Transparency and Accountability
Clear communication about data practices is essential for maintaining public trust in autonomous vehicle technology. Manufacturers should provide comprehensive information about data collection scope, usage parameters, and access protocols. Establishing unambiguous accountability structures ensures responsible data management practices.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Developing comprehensive regulations and industry standards for autonomous vehicle data management is crucial. These should address data collection limits, retention periods, and user consent requirements. International coordination is necessary to establish consistent standards across different regulatory environments.
Ethical Considerations in Data Use
The ethical dimensions of autonomous vehicle data usage involve complex questions about algorithmic bias, individual privacy impacts, and manufacturer liability. Developing clear ethical guidelines is essential for responsible technology development and deployment.
Data Breaches and Mitigation Strategies
Like all data-intensive systems, autonomous vehicles face inherent breach risks. Effective risk management requires regular security evaluations, penetration testing, and comprehensive incident response plans. Ongoing adaptation to emerging threats is necessary to maintain data security and user privacy.