Understanding Crankshaft Position Sensors
Crankshaft position sensors (CKP) are crucial components in internal combustion engines. These sensors play a vital role in detecting the precise angular position of the crankshaft. They accomplish this by utilizing magnetic fields and inductive principles, providing a signal to the engine control unit (ECU) that dictates the precise timing of fuel injection, ignition, and other engine functions. Accurate crankshaft position data is the cornerstone of efficient and reliable engine operation.
The output signal from the CKP sensor is directly related to the crankshaft's rotation. This signal is essential for the ECU to synchronise various engine components, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing emissions.
The Importance of Accurate Engine Timing
Precise engine timing is fundamental to optimal engine performance. It ensures that the fuel and air mixture is ignited at the precise moment of the crankshaft's rotation. This precise timing allows for maximum power output, efficient fuel consumption, and minimal emissions. Deviations from accurate timing can lead to significant performance issues, including reduced power, rough idling, and even engine damage.
Maintaining proper timing also ensures consistent combustion within the engine cylinders. This consistency is vital for smooth operation and longevity of the engine's components.
How Crankshaft Position Sensors Work
Crankshaft position sensors typically utilize a magnetic or inductive method to detect the position of the crankshaft. A toothed wheel or similar component attached to the crankshaft interrupts a magnetic field, generating a signal that is interpreted by the sensor. This signal is then translated into a precise angular position measurement for the engine control unit.
The sensor's output is a fluctuating signal directly related to the speed and position of the crankshaft. This signal is essential for the ECU to coordinate various engine functions.
The Role of the Engine Control Unit (ECU)
The engine control unit (ECU) is the brain of the engine. It receives the data from the crankshaft position sensor, along with other sensor inputs, to calculate the precise timing for fuel injection, ignition, and other crucial engine functions. The ECU's role is pivotal in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency based on real-time data.
The ECU constantly monitors the sensor data, adjusting the timing parameters accordingly to maintain optimal engine operation in different driving conditions.
Diagnosing Crank Position Sensor Issues
Malfunctioning crankshaft position sensors can manifest in various ways. Diagnosis often involves checking the sensor's output signal using a diagnostic tool to identify any irregularities in the signal pattern. These irregularities can be indicative of a faulty sensor or a problem with the wiring or connections. Troubleshooting often requires careful analysis of the sensor's output to pinpoint the exact source of the issue.
If the sensor is faulty, it may lead to misfiring, loss of power, or engine stalling. A faulty sensor, therefore, needs prompt attention to avoid potential further damage to the engine.
Maintaining Crankshaft Position Sensor Performance
Regular maintenance of the crankshaft position sensor is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. This includes ensuring the sensor is properly connected and secured, and that the wiring is intact and free from damage. Periodic checks for damage, debris, or corrosion around the sensor itself can also help maintain proper functionality.
Keeping the area around the sensor clean and free from debris minimizes the risk of interference, ensuring accurate and reliable data transmission.
The Impact on Engine Performance
Accurate crankshaft position data is essential for optimizing engine performance across various operating conditions. Precise timing allows for efficient combustion, maximizing power output and minimizing fuel consumption. Conversely, inaccurate readings lead to misfires, reduced power, and potentially damage to engine components. Therefore, maintaining a functional CKP sensor is crucial for the overall health and performance of the engine.
The sensor's role in synchronizing different engine components—like fuel injection and ignition—directly affects the engine's overall efficiency and power delivery, highlighting its importance in modern automotive technology.
Streamlining the supply chain is crucial for achieving significant cost savings. By implementing robust inventory management systems, businesses can minimize holding costs and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Efficient logistics planning, including strategic partnerships with reliable carriers and optimized transportation routes, can drastically reduce transportation expenses. This approach also enhances delivery speed and customer satisfaction, further contributing to the overall bottom line.
Troubleshooting Issues and Diagnosis
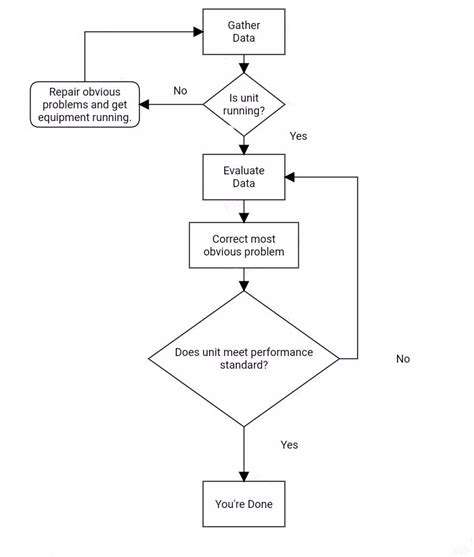
Identifying the Source of the Problem
Troubleshooting effectively hinges on pinpointing the root cause of the issue. A methodical approach, involving careful observation and data collection, is crucial. This might involve checking logs, reviewing system configurations, or even simulating the problem in a controlled environment. Understanding the specific symptoms and their relationship to potential causes is key to a successful resolution. The ability to isolate the problem area is often the most significant hurdle in the troubleshooting process.
A detailed analysis of the situation is essential. This involves documenting all relevant information, including error messages, system status, and user actions leading up to the problem. Thorough documentation allows for easier identification of patterns and potential correlations between different factors.
Hardware Diagnostics
If the issue relates to hardware, a series of checks can often reveal the problem. This may involve testing the power supply, checking connections, and verifying the functionality of peripheral devices. Often, a simple physical inspection can uncover loose cables or malfunctioning components. A visual inspection is an important first step.
It's critical to rule out hardware failures as the root cause. This might involve running diagnostic tools provided by the manufacturer or using specialized equipment to test individual components.
Software Configuration Checks
Software configuration errors are a frequent source of problems. Reviewing the configuration files and settings within the software applications involved is often necessary. Pay close attention to any unusual settings or recent modifications that may have contributed to the issue. Improperly configured software can lead to unexpected behavior and significant disruptions.
Ensuring that the software is up-to-date with the latest patches and updates is also important. Outdated software can introduce vulnerabilities or instability that can manifest as various issues.
Network Connectivity Evaluation
If the problem stems from network connectivity, testing the network connection is essential. This might involve checking network cables, verifying IP addresses, and ensuring proper routing configurations. Diagnosing network issues can be complex, requiring a systematic approach to identify the precise location of the problem. Tools like ping and traceroute can be valuable in this process.
User Interface Analysis
Examining user interface elements is important if the issue relates to user experience. This might involve checking for corrupted files, verifying the proper functioning of menus and buttons, and ensuring the interface is consistent with expectations. Thorough analysis of the UI can identify areas of concern or potential design flaws that are contributing to the difficulty users are experiencing.
Data Integrity Checks
Data corruption or inconsistencies can be a significant source of issues. Verifying the integrity of the data involved is important. This might involve checking for missing or duplicated files, verifying data formats, and ensuring data consistency across different systems. Proper data integrity is critical for maintaining accuracy and reliability.
Security and Access Controls
Security breaches or access restrictions can sometimes lead to issues. Reviewing access controls, user permissions, and security protocols is often required. Unintended security limitations may prevent access to necessary resources, causing significant disruptions. It is important to ensure that security measures are properly configured and enforced.