Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Connected car manufacturers must meticulously collect only the data absolutely necessary to fulfill their intended purpose. This principle of data minimization is crucial for GDPR compliance, preventing the accumulation of unnecessary personal information. For example, if a manufacturer collects location data for diagnostics, they should only retain the data required for that specific purpose and delete it promptly once the diagnostic process is complete. Furthermore, the purpose for collecting the data must be clearly defined and explicitly stated to the user, allowing them to understand how their data will be used and ensuring transparency.
Detailed documentation of data collection practices, including the specific types of data collected, the purposes for collection, and the retention periods, is essential. This documentation will serve as a valuable reference for demonstrating compliance and addressing any potential queries from data protection authorities or users. This thorough documentation should also be readily accessible to users, enabling them to understand their rights and how their data is handled.
User Consent and Transparency
Obtaining explicit and informed consent from users for data collection is paramount. Manufacturers should employ clear and easily understandable language in consent forms, explaining precisely how the collected data will be used and processed. The consent process should be straightforward, allowing users to easily opt-in or opt-out of specific data collection practices. This includes providing users with the option to manage their data preferences and control the level of data collected, ensuring they have agency over their personal information.
Transparency is vital. Users should be informed about the specific data collected, the purposes for its use, and the potential consequences of not providing consent. This transparency fosters trust and enables users to make informed decisions about the data they share with the connected car manufacturer. Providing detailed information about data security measures and potential risks is also part of this transparency, ensuring users are aware of the safeguards in place to protect their personal information.
Data Security and Protection
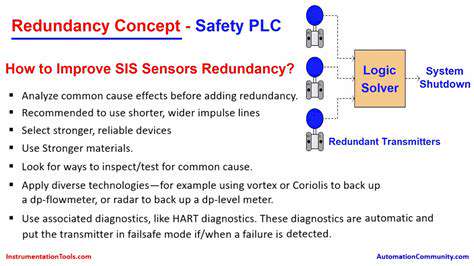
Implementing robust data security measures is critical to protect user data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This includes employing appropriate technical and organizational measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Manufacturers should have clear procedures for incident response in case of a data breach, enabling a swift and effective response to minimize potential harm to user data and maintain trust. Adequate security measures should be in place for both the collection and storage of data, as well as for the transmission of data between different systems.
Regular security assessments and vulnerability testing are vital to identify potential weaknesses and proactively address them. Manufacturers should maintain an up-to-date security policy that aligns with industry best practices and data protection regulations, ensuring continuous improvement in data protection. This includes training employees on data security protocols and procedures to mitigate risks and foster a security-conscious culture within the organization.
Data Minimization and Security Measures: Protecting Sensitive Information

Data Minimization Principles
Data minimization is a core principle in data protection, emphasizing the collection and processing of only the minimum amount of personal data necessary for specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes. This principle seeks to limit the potential for misuse or unauthorized access to personal information. It's not just about reducing the volume of data, but also about carefully considering what data is truly required and why.
Implementing data minimization requires a thorough understanding of the purpose for collecting each piece of data. A clear articulation of these purposes, and how the data will be used, is essential for demonstrating compliance with data protection regulations.
Defining Explicit and Legitimate Purposes
Explicit and legitimate purposes for data processing are crucial for data minimization. These purposes should be clearly defined and documented, outlining exactly how the data will be used. For example, if collecting email addresses, the purpose should be clearly stated as being for sending newsletters or marketing communications, not for unrelated purposes.
Ensuring the data collected is directly relevant to the stated purpose is paramount for maintaining data security and minimizing risks. This approach helps prevent the unintentional collection of excessive or unnecessary information.
Security Measures for Stored Data
Robust security measures are essential for protecting stored data, regardless of the amount. These measures should include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication is vital for safeguarding sensitive information. Regularly reviewing and updating security protocols is also important to address evolving threats.
Data Retention Policies
Clearly defined data retention policies are critical for minimizing the duration personal data is stored. These policies should outline specific criteria for data deletion or archiving, ensuring data is not retained longer than necessary.
Establishing clear retention schedules and procedures is essential for compliance with data protection regulations. This helps prevent the accumulation of unnecessary data and limits the risk of data breaches.
Data Subject Access Rights
Data subjects have the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal data. Providing clear mechanisms for data subjects to exercise these rights is vital for promoting transparency and accountability.
Secure Data Transfer Protocols
When transferring data, secure protocols and encryption methods must be employed. This ensures data confidentiality and integrity during transmission and storage.
Data encryption throughout the entire data lifecycle is a key element for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. Using secure communication channels, like HTTPS, is crucial for protecting data during transit.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are necessary to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. These audits should evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures and identify areas for improvement.
Proactive security assessments and audits are essential for maintaining a strong security posture and responding to evolving threats. These assessments allow organizations to continuously improve their security practices and mitigate risks.
The existence and characteristics of Jupiter's core are still actively debated among scientists. Is it a solid core, a dense mix of heavier elements, or something else entirely? Juno's gravity measurements are providing valuable data that could help answer these questions.
User Rights and Data Portability: Empowering the Driver
Understanding User Rights
In the interconnected world of modern vehicles, understanding user rights is paramount. drivers have a right to know what data is being collected about their driving habits, the purposes for which it's being used, and how it's being protected. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their personal information and the features they choose to utilize within their connected car.
Furthermore, clear and accessible information regarding data retention policies, data security measures, and potential third-party data sharing is essential for building trust and transparency. Drivers should have the ability to understand not just the mechanics of data collection, but also the potential implications for their personal lives and privacy.
Data Portability: Taking Control of Your Information
Data portability is a critical aspect of user rights, enabling drivers to access, transfer, and reuse their personal data collected by the connected car system. This feature allows drivers to download their driving data, such as trip history, fuel efficiency records, and maintenance logs, for their own review and use. This control over personal information is crucial for maintaining ownership and agency over the data generated by their vehicle.
Such portability offers drivers the flexibility to transfer their data to alternative services or platforms. For instance, a driver might want to analyze their driving data to optimize fuel consumption or compare it with other drivers to identify areas for improvement. The ability to take control of this data and utilize it for personal benefit is a significant step forward in empowering the driver and fostering data ownership.
Protecting Sensitive Information: Data Security Measures
Connected car systems collect a wealth of personal information, including location data, driving habits, and even vehicle maintenance records. Robust data security measures are absolutely essential to protect this sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Implementing encryption, secure storage, and access controls are critical to maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of driver information.
The privacy and security of driver data should be paramount. Data breaches can have significant consequences, ranging from identity theft to financial losses. Connected car manufacturers must take proactive steps to safeguard driver information, ensuring that robust security protocols are in place to mitigate potential risks and maintain trust.
Transparency and Accountability: Driving Informed Decisions
Transparency in data practices is crucial for building trust between drivers and connected car manufacturers. Clear and easily understandable policies regarding data collection, usage, and sharing practices should be readily available to drivers. This transparency empowers them to make informed decisions about the features they choose to use and the level of data they are comfortable sharing. Drivers should also have access to mechanisms for complaint resolution and recourse in case of data breaches or violations of their rights.
Accountability is equally important. Manufacturers should be held accountable for the security and responsible use of the data they collect. Clear lines of communication and readily available channels for feedback and redress are essential to foster a sense of responsibility and accountability in the industry. Drivers should feel empowered to voice concerns and have them addressed effectively.
Future Trends and Challenges: Adapting to an Evolving Landscape

Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is poised to revolutionize various sectors, presenting both opportunities and challenges. AI-powered automation will reshape industries, demanding new skill sets and potentially leading to job displacement in certain areas. Companies will need to adapt to these changes by investing in training and upskilling programs to ensure their workforce remains competitive. The increasing use of AI in decision-making processes will also necessitate careful consideration of ethical implications and biases in algorithms.
Further advancements in data analytics and the increasing volume and complexity of data will require robust infrastructure and expertise. The ability to effectively collect, process, and interpret this data will be paramount for informed decision-making and competitive advantage. This also brings up the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data from breaches and misuse.
Global Economic Shifts and Their Implications
The global economy is experiencing significant shifts, including rising protectionism, geopolitical uncertainties, and fluctuating exchange rates. These factors can create instability and uncertainty for businesses operating in international markets. Navigating these complexities and adapting to new trade agreements and regulations is crucial for maintaining profitability and growth.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
The growing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable practices is impacting businesses across sectors. Consumers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products and services, and companies are under pressure to adopt sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This trend is likely to drive innovation and investment in renewable energy, sustainable materials, and circular economy models.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The competition for skilled talent is intensifying, and businesses are facing challenges in attracting and retaining top performers. Attracting and retaining employees requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing competitive compensation, robust benefits packages, and a supportive work environment. Investing in employee development and fostering a culture of learning and growth is vital for creating a motivated and engaged workforce.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, and businesses must adapt to new laws and regulations to ensure compliance. Staying informed about emerging legislation and adapting internal processes and procedures is essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining a positive reputation. Compliance with regulations can be complex, demanding dedicated resources and expertise to ensure adherence to all applicable standards.
Innovation and Disruption
Disruptive technologies and innovative business models are emerging at an accelerated pace. Companies need to foster an environment that encourages creativity and experimentation to stay ahead of the curve. Embracing innovation and embracing new ideas is vital for long-term success and adaptability in a rapidly changing marketplace. This necessitates a willingness to take calculated risks and invest in research and development.