Minimizing Waste and Resource Consumption
Sustainable manufacturing hinges on minimizing waste and maximizing the efficient use of resources. This requires a fundamental shift in thinking, moving away from a take-make-dispose linear model toward a circular economy. Companies must prioritize the use of recycled and renewable materials, reducing the need for virgin resources. Implementing closed-loop systems, where waste is repurposed or reused as input for new products, significantly reduces environmental impact and fosters a more sustainable production cycle. This approach not only conserves resources but also reduces the environmental burden of extracting and processing raw materials.
Waste reduction extends beyond material use. Optimizing production processes to minimize energy consumption is crucial. Implementing energy-efficient machinery, utilizing renewable energy sources, and improving operational efficiency all contribute to a smaller carbon footprint. Careful consideration of the entire lifecycle of a product, from raw material extraction to disposal, is vital. Minimizing waste at each stage, from design and manufacturing to packaging and transport, significantly contributes to a more sustainable production process.
Promoting Circularity and Regenerative Practices
A core principle of sustainable manufacturing is promoting a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled endlessly. Companies must move away from the traditional linear model of production, which involves extracting resources, manufacturing products, and ultimately disposing of waste. This change requires a complete redesign of manufacturing processes, emphasizing the reuse and recycling of materials within the production cycle. By designing products with disassembly and reuse in mind, companies can significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with waste disposal and resource extraction.
Beyond circularity, regenerative practices are essential. This involves actively restoring and enhancing the environment. For example, using sustainable forestry practices to replenish forests, implementing water conservation measures, and supporting biodiversity are crucial components of regenerative manufacturing. Sustainable manufacturing is not simply about minimizing harm; it's about actively contributing to a healthier planet. Companies should strive to use eco-friendly production methods that minimize their impact on the environment at every stage of the manufacturing process.
Another key aspect of regenerative practices is the incorporation of ecological principles into product design. This includes using bio-based materials, designing for durability and repairability, and promoting product longevity. By focusing on these principles, businesses can create products that have a minimal impact on the environment throughout their entire life cycle.
Implementing these regenerative practices requires a shift in mindset from a purely profit-driven approach to one that considers the environmental and social impacts of production decisions. Companies must consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal, and integrate environmental considerations into every aspect of their operations.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a production system that not only reduces harm but actively contributes to the health and well-being of the planet. This requires a fundamental reimagining of how we produce goods and a commitment to sustainability throughout the entire value chain.
Embracing Circular Economy Principles in Automotive Production
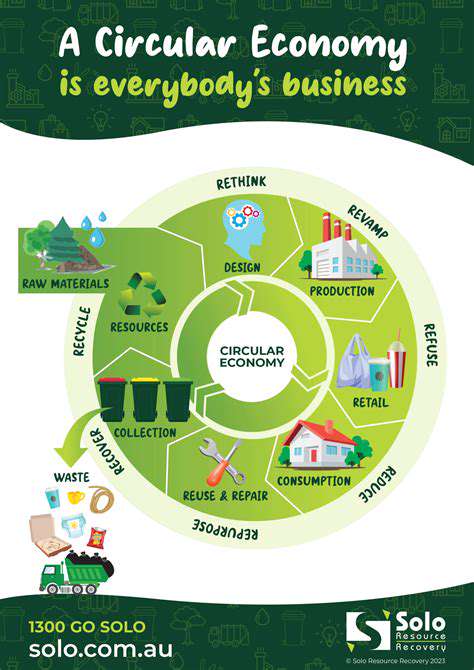
Understanding the Principles of Circular Economy
The circular economy represents a fundamental shift from the traditional linear take-make-dispose model to a more sustainable and restorative approach. It emphasizes the importance of designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. This approach acknowledges that resources are finite and that current practices are unsustainable in the long term. By focusing on reuse, repair, and recycling, the circular economy aims to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency. This is a complex system, requiring collaboration among businesses, consumers, and governments to succeed.
A key principle within the circular economy is the concept of product lifecycles. Instead of products being designed for a single use and then discarded, circular economy principles encourage the design of products that can be easily repaired, reused, or recycled at the end of their initial use. This reduces the demand for virgin resources, lessening the environmental impact associated with extraction and manufacturing. The goal is to prolong the useful life of products and materials, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
Implementing Circular Economy Practices
Implementing circular economy principles across various industries requires a multifaceted approach. Businesses must actively consider design for durability and repairability, fostering a culture of resource efficiency within their operations. This includes incorporating recycled materials into production processes and exploring innovative methods for product recovery and reuse. A major aspect of this is the development of innovative business models, such as product-as-a-service and sharing platforms, which can extend the lifespan of products and encourage collaborative consumption.
Consumers play a vital role in embracing circular economy principles. By making conscious choices about the products they purchase, opting for durable and repairable items, and actively participating in recycling programs, they can significantly contribute to a more sustainable future. Adopting a mindset of reuse and repair, instead of immediate replacement, is crucial in reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency within their daily lives. Adopting these practices not only benefits the environment but also fosters a more resilient and sustainable economy.
Government policies and regulations can also play a pivotal role in driving the transition towards a circular economy. Subsidies for businesses that implement circular economy practices and incentives for consumers who choose sustainable options can accelerate adoption. Clearer regulations on waste management and product design standards can further encourage businesses to prioritize sustainability and resource efficiency.
Ultimately, the circular economy requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders. Businesses, consumers, and governments must work together to support and implement these principles, creating a system that is both environmentally sound and economically viable.
Sustainable Material Sourcing and Selection

Ethical Considerations in Sourcing
Sustainable material sourcing extends beyond simply choosing environmentally friendly materials. It encompasses a crucial ethical dimension, demanding transparency and fair labor practices throughout the supply chain. Companies must actively seek to understand the conditions under which materials are produced, ensuring workers' rights are respected, and communities are not exploited. This includes fair wages, safe working environments, and the absence of child labor. A commitment to ethical sourcing is not just a moral imperative but also a vital element of building a strong and trustworthy brand.
Understanding the environmental impact of various materials is essential, but it's equally important to consider the human impact. Sourcing materials ethically involves a commitment to responsible labor practices, ensuring fair compensation, safe working conditions, and the absence of exploitative labor practices. This commitment to ethical labor standards extends to all stages of the supply chain, from the initial extraction of raw materials to the final product assembly.
A company's reputation hinges on its commitment to ethical sourcing. Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social consequences of their purchases and are more likely to support businesses that prioritize ethical sourcing. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, companies not only build a positive brand image but also create a more sustainable and equitable global supply chain.
Environmental Impact Assessment
A comprehensive assessment of the environmental impact of materials is a critical component of sustainable sourcing. This includes evaluating the entire lifecycle of a material, from its extraction to disposal. Factors like water usage, carbon emissions, and waste generation are crucial considerations. Careful analysis allows businesses to identify areas for improvement and to make informed choices that minimize their environmental footprint.
Quantifying the environmental impact of different materials is essential for making informed decisions. This involves a thorough analysis of the embodied energy in a material, considering the energy required to extract, process, and transport it. Evaluating the environmental impact of each stage of the material's lifecycle, from extraction and processing to manufacturing and disposal, is key to making informed decisions about sustainable sourcing.
Ultimately, a thorough environmental impact assessment is vital for identifying potential environmental risks and opportunities for improvement. By understanding the full environmental impact of a material, companies can make more sustainable choices and reduce their environmental footprint across the entire supply chain. In addition, this approach allows businesses to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
Understanding the environmental impact of various materials is a fundamental aspect of sustainable sourcing. Analyzing the carbon footprint of a material is crucial. This analysis allows for the selection of materials with a lower carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain.