Defining Standardization
Standardization in EV charging networks is crucial for seamless user experience across different providers. A standardized approach ensures that a variety of EV charging stations, from different manufacturers and operators, can be easily accessed and used by drivers. This eliminates the need for drivers to learn multiple systems and protocols, fostering a more user-friendly and integrated charging experience. Without standardization, interoperability between various charging networks would be significantly hampered, leading to frustration and potentially limiting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
This standardization involves agreeing on common technical specifications for connectors, communication protocols, and data formats. These common standards facilitate the development of a unified charging infrastructure that caters to the diverse needs of EV drivers, regardless of the brand of their electric vehicle.
The Importance of Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different systems to work together seamlessly. In the context of EV charging, it means that an EV charger from one network should be compatible and usable with an account from another network. This is vital for maximizing the convenience and accessibility of EV charging. Drivers should be able to use a single charging account to access a vast network of charging stations, without the hassle of multiple subscriptions or different login procedures.
Benefits of a Standardized Network
A standardized EV charging network offers numerous benefits, ranging from increased customer satisfaction to economic growth. Drivers experience convenience and ease of use, which fosters trust and encourages wider adoption of electric vehicles. It also creates a more favorable investment environment for charging station infrastructure development, as companies can confidently invest in a network that is compatible and interoperable with other providers.
Standardization attracts more participation from manufacturers and operators, leading to a larger and more robust charging network. A unified approach also simplifies the development and maintenance of the charging infrastructure, reducing overall costs and improving efficiency.
Challenges in Achieving Standardization
Despite the clear benefits, achieving standardization in EV charging networks presents several challenges. Differing technical specifications, varying priorities among stakeholders, and the need to maintain compatibility with legacy systems are some examples. Overcoming these hurdles requires collaboration and compromise from various stakeholders, including charging station manufacturers, network operators, and automotive manufacturers. A collaborative approach that prioritizes interoperability and consumer needs is essential to overcome these obstacles.
Impact on EV Adoption Rates
Standardization and interoperability have a significant impact on the adoption rates of electric vehicles. A seamless and integrated charging experience encourages more people to switch to electric vehicles, as the hassle of navigating different charging networks is eliminated. As more drivers experience the convenience of a unified charging network, the demand for electric vehicles will increase, fostering a transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
Long-Term Vision for EV Charging
The long-term vision for EV charging networks involves a fully interconnected and standardized infrastructure. This future envisions a world where drivers can seamlessly charge their EVs at any station across the network, regardless of the provider. This vision necessitates continuous collaboration, innovation, and adaptation to evolving technological advancements. This forward-thinking approach will drive the growth of the EV market and the transition towards a greener transportation future.

Future Trends and Challenges: Integrating Sustainability and Innovation
Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a unique opportunity to leverage sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. This includes exploring alternatives to traditional materials like lithium, which has ethical and environmental concerns associated with its extraction. Innovations in battery technology, such as the development of solid-state batteries and advancements in recycling technologies for existing battery chemistries, are crucial for reducing the environmental footprint of EV production and ensuring long-term sustainability. The development of recycled materials and the integration of these materials into EV components will be vital in lowering the environmental impact of the entire lifecycle of EVs.
Moving beyond the battery itself, sustainable manufacturing practices are essential. This encompasses utilizing recycled metals and plastics in the construction of EV bodies, employing energy-efficient production processes, and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing chain. The adoption of circular economy principles within the EV industry will be key in minimizing environmental damage and maximizing resource utilization.
Charging Infrastructure and Accessibility
Expanding and optimizing charging infrastructure is paramount for widespread EV adoption. This includes developing smart charging networks that can predict demand, optimize energy distribution, and facilitate seamless charging experiences for drivers. Public charging stations need to be strategically located in residential areas, workplaces, and along major transportation routes to ensure convenient access for all users. The integration of renewable energy sources into charging stations will be vital for reducing the carbon footprint of EV charging and aligning with broader sustainability goals. Government incentives and policies that encourage the development of EV charging infrastructure are crucial for enabling the transition and ensuring equitable access for all.
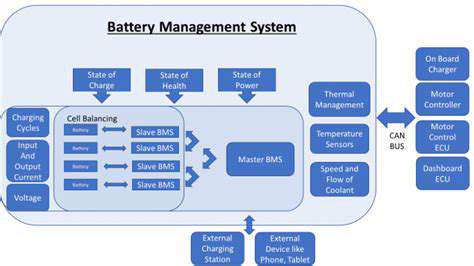
Addressing the geographical disparities in charging station availability will also be a significant challenge. Strategies for deploying charging stations in underserved communities and rural areas need to be considered to ensure equitable access to EV technology. Furthermore, developing innovative charging solutions, such as wireless charging technologies and advanced battery management systems, is essential for improving charging efficiency and reducing the time spent charging.
Innovations in Battery Technology and Charging Efficiency
Continued advancements in battery technology are essential for improving EV range, charging speed, and overall performance. This includes research and development focused on higher energy density batteries, faster charging times, and longer lifespans. The development of new battery chemistries that are more sustainable and less reliant on rare earth materials is crucial for the long-term viability of EVs. Research into solid-state batteries, which offer potential advantages in terms of safety and energy density, will be a key area of focus. These advancements will enhance the overall user experience and accelerate the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Improving charging efficiency is another critical area of innovation. This includes optimizing charging protocols to minimize energy loss during the charging process. Developing more efficient charging infrastructure, such as DC fast chargers with advanced control systems, will also play a significant role in accelerating the charging process. Furthermore, the integration of smart charging technologies that can dynamically adjust charging rates based on grid conditions and user preferences is essential for optimizing energy consumption and reducing the strain on the electricity grid.