Recyclable Metals and Alloys for Enhanced Circularity

Recycling Aluminum: A Sustainable Solution
Aluminum is a widely used metal in various industries, and its recyclability is a crucial factor in sustainable practices. Recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy compared to extracting it from raw materials, saving substantial amounts of energy and reducing the environmental impact. This process also conserves natural resources, minimizing the strain on the planet's finite reserves of bauxite, the primary ore used to produce aluminum.
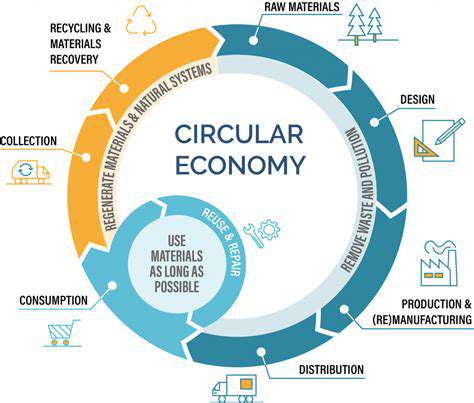
The recycling process is highly efficient, with a large percentage of aluminum products being recycled and reused. This closed-loop system contributes to a circular economy, where materials are continuously reused, reducing waste and promoting environmental responsibility. The benefits of aluminum recycling are substantial, not only for the environment but also for the economy, as it creates jobs and stimulates economic growth in the recycling sector.
Copper Recycling: A Vital Component
Copper is another crucial metal with significant recycling potential. Its extensive use in electrical wiring, plumbing, and various industrial applications makes its recyclability essential for environmental sustainability. Copper recycling plays a vital role in reducing the demand for new copper production, thereby minimizing the negative environmental impacts associated with mining and processing raw materials.
The high purity and consistent quality of recycled copper make it a preferred choice for many applications. This ensures that recycled copper maintains its valuable properties, making the recycling process economically viable and environmentally sound.
Steel Recycling: A Cornerstone of Sustainability
Steel, a ubiquitous material in construction, manufacturing, and transportation, presents a significant opportunity for recycling. The recycling process for steel is relatively straightforward and energy-efficient, making it a crucial component of a sustainable materials management strategy. Steel recycling reduces the need for new iron ore extraction, minimizing the environmental footprint associated with mining and processing this vital resource.
Precious Metal Recovery: A Focus on Value
Recycling precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of mining and improving resource efficiency. The recovery of these metals from discarded electronics, jewelry, and industrial waste is a valuable endeavor. These metals are often embedded in complex alloys, requiring specialized techniques for efficient and environmentally sound recovery.
The high value of these metals motivates the development of advanced recycling technologies, further promoting the economic viability and environmental sustainability of the process. This focused approach on precious metal recovery is a significant step towards a more circular economy.
Nickel and its Alloys: A Growing Importance
Nickel, a vital component in various alloys used in batteries, stainless steel, and other applications, is increasingly important in industries like renewable energy. The recycling of nickel and its alloys is essential for reducing the environmental impact of mining and maintaining the supply of this crucial metal. Recycling nickel allows for the recovery of valuable materials and minimizes the environmental harm associated with the extraction and processing of new nickel ore.
Advancements in nickel recycling technologies are constantly improving, contributing to greater efficiency and sustainability in the process. This continuous improvement is vital for meeting the growing demand for nickel in various sectors.
Magnesium and its Alloys: Emerging Opportunities
Magnesium and its alloys, known for their lightweight properties, are gaining traction in various sectors, including automotive and aerospace. The recycling of magnesium and its alloys presents an emerging opportunity for sustainable material management. The challenges in magnesium recycling lie primarily in the recovery of pure magnesium from alloys, often requiring sophisticated and energy-intensive processes.
However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of magnesium recycling, making it a potential solution for future sustainability challenges. This area is ripe for innovation and holds significant promise for the future.