Automotive OEMs: Leading the Charge
Automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are at the forefront of the connected car ecosystem, driving innovation and shaping the future of mobility. They are responsible for integrating various technologies into their vehicles, from infotainment systems and navigation to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and telematics. Their role extends beyond simply developing the hardware; they are also crucial in defining the software architecture and user interfaces, and in establishing partnerships with other ecosystem players to ensure a seamless user experience and a robust, secure platform. OEMs are critical to the success of the connected car ecosystem, setting standards and influencing market trends. Their investment in research and development is essential for pushing the boundaries of connected car technology.
OEMs are also heavily involved in the development of standards and protocols for communication between vehicles and external systems. This includes establishing secure communication channels, ensuring interoperability across different manufacturers' platforms, and facilitating data sharing among various stakeholders. Their influence on the entire value chain is undeniable, as they dictate the features and functionalities that will be available to consumers and influence the evolution of the connected car market.
Tier 1 Suppliers: The Backbone of Innovation
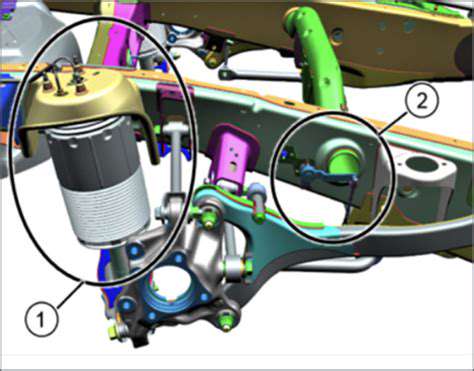
Tier 1 suppliers play a pivotal role in the connected car ecosystem, acting as crucial partners for OEMs. These companies specialize in providing critical components and modules for vehicle integration, including electronics, sensors, and communication systems. Their expertise in engineering and manufacturing ensures the reliability and performance of connected car technologies, from the embedded systems to the intricate software components. This crucial role of Tier 1 suppliers in the value chain is essential for enabling the seamless operation of various connected car features.
Furthermore, Tier 1 suppliers are often at the forefront of developing new technologies. By investing in research and development, they create innovative solutions that enhance the performance and functionality of connected car systems. This continuous innovation is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving automotive industry.
Telematics Providers: Connecting the Dots
Telematics providers are indispensable to the connected car ecosystem, facilitating communication between vehicles and the cloud. They offer solutions for collecting and analyzing vehicle data, providing insights into driving behavior, maintenance needs, and potential safety concerns. This data collection is crucial for improving vehicle safety, optimizing maintenance schedules, and personalizing the driving experience. Their ability to securely transmit and process vast amounts of data is essential for the smooth operation of various connected car functionalities.
Software Developers: Crafting the Experience
Software developers play a vital role in the connected car ecosystem, crafting the user interfaces and functionalities that enhance the driving experience. From designing intuitive infotainment systems to developing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) software, their expertise is paramount. They are responsible for creating the seamless integration between different technologies and for delivering a compelling user experience. The development of sophisticated algorithms for various applications, such as navigation, entertainment, and safety features, relies heavily on the expertise of software developers.
Their contributions extend beyond the development of individual applications. They play a critical role in ensuring the interoperability of different systems and platforms, creating a cohesive and consistent user experience across different connected car features. The success of the connected car ecosystem hinges on the innovative spirit and expertise of software developers.
Data Providers and Service Providers: Fueling the Ecosystem
Data providers and service providers are critical to the success of the connected car ecosystem. They furnish the data necessary for enhancing the functionality and performance of connected car features. This includes providing real-time traffic information, weather updates, and other relevant data points that enhance the driving experience. Their role is crucial for enabling features such as real-time navigation and safety alerts. Their data and services are essential for delivering a seamless and intelligent driving experience.
Service providers, such as insurance companies and mobility platforms, also play a critical role in the connected car ecosystem. They leverage the data generated by connected cars to offer innovative services, including personalized insurance plans based on driving behavior and mobility solutions that optimize routes and parking. This integration of data and services significantly enhances the overall value of the connected car experience for consumers.
The Supporting Cast: Technology Providers
Software Development Kits (SDKs)
Software Development Kits (SDKs) are crucial components in the connected car ecosystem. These tools provide developers with the necessary resources and frameworks to build and integrate applications into the vehicle's operating system. SDKs typically include APIs, libraries, and examples that facilitate the creation of features like in-car infotainment systems, navigation, and telematics. Efficient and well-documented SDKs contribute significantly to the rapid development and deployment of new connected car functionalities, empowering both established and emerging players in the automotive industry.
The quality and comprehensiveness of an SDK directly impact the speed and cost-effectiveness of development. A robust SDK fosters innovation by reducing the learning curve for developers, enabling them to focus on feature enhancements and user experience improvements rather than wrestling with complex underlying technologies.
Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Cloud-based platforms are essential for managing the massive amounts of data generated by connected cars. These platforms provide the infrastructure for storing, processing, and analyzing the data, enabling features such as real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and personalized driving experiences. Reliable cloud services are critical for ensuring the security and availability of data, and they provide scalability to accommodate the growing number of connected vehicles on the road.
The choice of cloud infrastructure provider significantly impacts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the entire connected car ecosystem. Factors such as data security, regulatory compliance, and scalability requirements must be carefully considered during the selection process.
Telematics Providers
Telematics providers play a vital role in collecting and transmitting data from connected vehicles. Their services enable features like vehicle tracking, remote diagnostics, and fleet management solutions. Accurate and reliable telematics data is essential for enabling a wide range of applications, from improving safety to optimizing vehicle maintenance. The quality of the telematics data and the reliability of the communication infrastructure are key factors in the success of connected car applications.
Mapping and Navigation Solutions
High-quality mapping and navigation solutions are fundamental to the connected car experience. These solutions provide real-time traffic updates, route optimization, and point-of-interest information. Accurate and up-to-date maps are essential for safe and efficient navigation, which is crucial for enhancing the overall user experience of connected vehicles. The ability to integrate with various navigation systems and to adapt to dynamic road conditions is crucial for the success of these solutions.
Partnerships with mapping providers are essential to ensure comprehensive coverage and up-to-date information. The continuous improvement and accuracy of these maps directly impact the safety and convenience of drivers.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication Systems
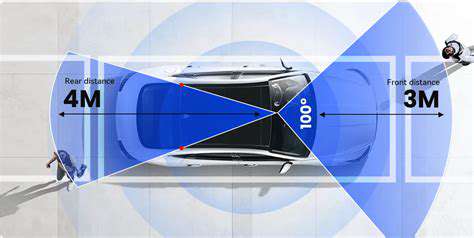
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication systems enable communication between vehicles and their surroundings, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and infrastructure. These systems are crucial for enhancing safety by providing real-time information about potential hazards and enabling advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Reliable and secure V2X communication is essential for maximizing the safety and efficiency of connected vehicles on the road. The ability to seamlessly integrate V2X communication protocols into various vehicle platforms is key to widespread adoption.
Payment Gateways and Financial Services
Payment gateways and financial services are critical for handling transactions related to connected car services, such as subscription fees, in-car purchases, and insurance claims. Secure and reliable payment processing is essential for maintaining trust and facilitating seamless transactions within the ecosystem. The integration of financial services into the connected car experience enhances the overall user experience and expands the range of services offered.
Security Providers and Cyber-Security Solutions
Security providers and cyber-security solutions are paramount in protecting connected vehicles from potential threats. The increasing reliance on connected technologies exposes vehicles to new vulnerabilities, making robust security measures essential for safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. This includes protecting the vehicle's communication systems, onboard data, and user privacy. A comprehensive approach to security, involving both hardware and software solutions, is necessary to ensure the safety and integrity of the connected car ecosystem.
The Moon, our celestial neighbor, holds a wealth of untapped resources that could revolutionize our technological and economic landscape. Lunar resource extraction is poised to become a critical component of future space exploration and development, offering a sustainable source of raw materials for various applications. Understanding the potential of these resources and the challenges involved is crucial for realizing this ambitious goal.
The Gatekeepers: Connectivity Providers and Infrastructure

Gatekeeper Functionalities
Gatekeepers, in the context of connectivity provision, act as intermediaries, managing access and controlling the flow of information and resources. They play a crucial role in ensuring security, reliability, and efficiency of the network. These functionalities are essential for managing the diverse needs of various users and applications. From authentication to traffic shaping, gatekeepers ensure a smooth and secure experience for all connected parties.
A key aspect of gatekeeper functionality is the ability to prioritize traffic based on various criteria. This allows for efficient resource allocation and ensures critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth. Furthermore, gatekeepers often integrate with other systems, providing a seamless transition for data and services across different platforms. This integration capability is a critical component for a robust and scalable network infrastructure.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in any connectivity provision system, and gatekeepers are instrumental in upholding this principle. Robust authentication mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. This includes implementing encryption protocols to safeguard data transmission and employing intrusion detection systems to identify and mitigate potential threats. Gatekeepers must also be regularly updated with the latest security patches to maintain their effectiveness against evolving cyber threats.
Protecting sensitive data is a top priority for any gatekeeper system. Implementing access control lists and other security measures is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of resources. Regular audits and security assessments are vital to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the system's ongoing security posture.
Scalability and Reliability
Connectivity provision systems must be able to adapt to increasing demands. Gatekeepers need to be designed with scalability in mind to handle growing numbers of users and devices without compromising performance. Redundancy and failover mechanisms are critical components for maintaining reliability, ensuring minimal disruption in the event of hardware or software failures.
Scalability is crucial for handling future growth in demand. Gatekeepers must be able to accommodate a significant increase in the number of connections and data volume without experiencing performance degradation. Redundancy ensures high availability, minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime, which is essential for mission-critical applications relying on the connectivity provided.
Integration and Interoperability
Effective connectivity provision relies heavily on seamless integration with existing systems and technologies. Gatekeepers should be designed with open APIs and protocols to facilitate interoperability with various platforms and applications. This allows for a consistent user experience and avoids creating isolated silos of data and services. This is crucial for a smooth and efficient user experience, allowing for easy integration with other services.
A well-designed gatekeeper system ensures a consistent user experience across all platforms and applications. The ability to seamlessly integrate with other systems is essential for a robust, flexible, and scalable connectivity provision solution. This interconnectedness allows for the efficient flow of data and services across different systems and minimizes user friction.